Spectral Analysis
Signal Processing Toolbox™ provides a family of spectral analysis functions and apps that let you characterize the frequency content of a signal. FFT-based nonparametric methods, such as Welch’s method or the periodogram, make no assumptions about the input data and can be used with any kind of signal. Parametric and subspace methods, such as Burg’s, covariance, and MUSIC, incorporate prior knowledge of the signal and can yield more accurate spectral estimates.
Compute power spectra of nonuniformly sampled signals or signals with missing samples using the Lomb-Scargle method. Measure signal similarities in the frequency domain by estimating their spectral coherence. Design and analyze Hamming, Kaiser, Gaussian, and other data windows.
Categories
- Spectral Estimation
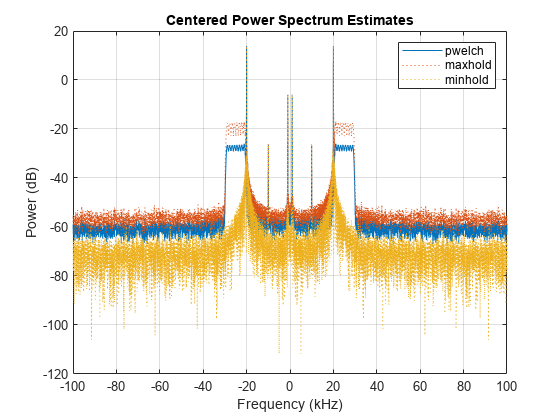
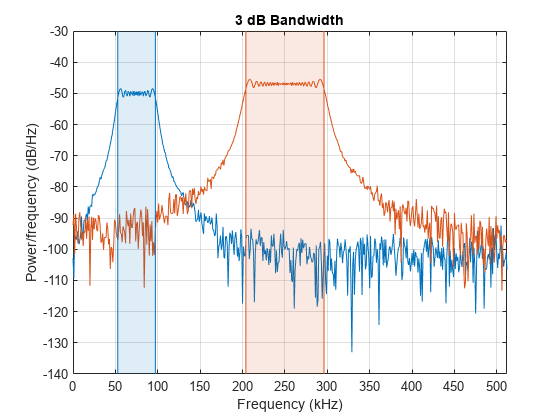
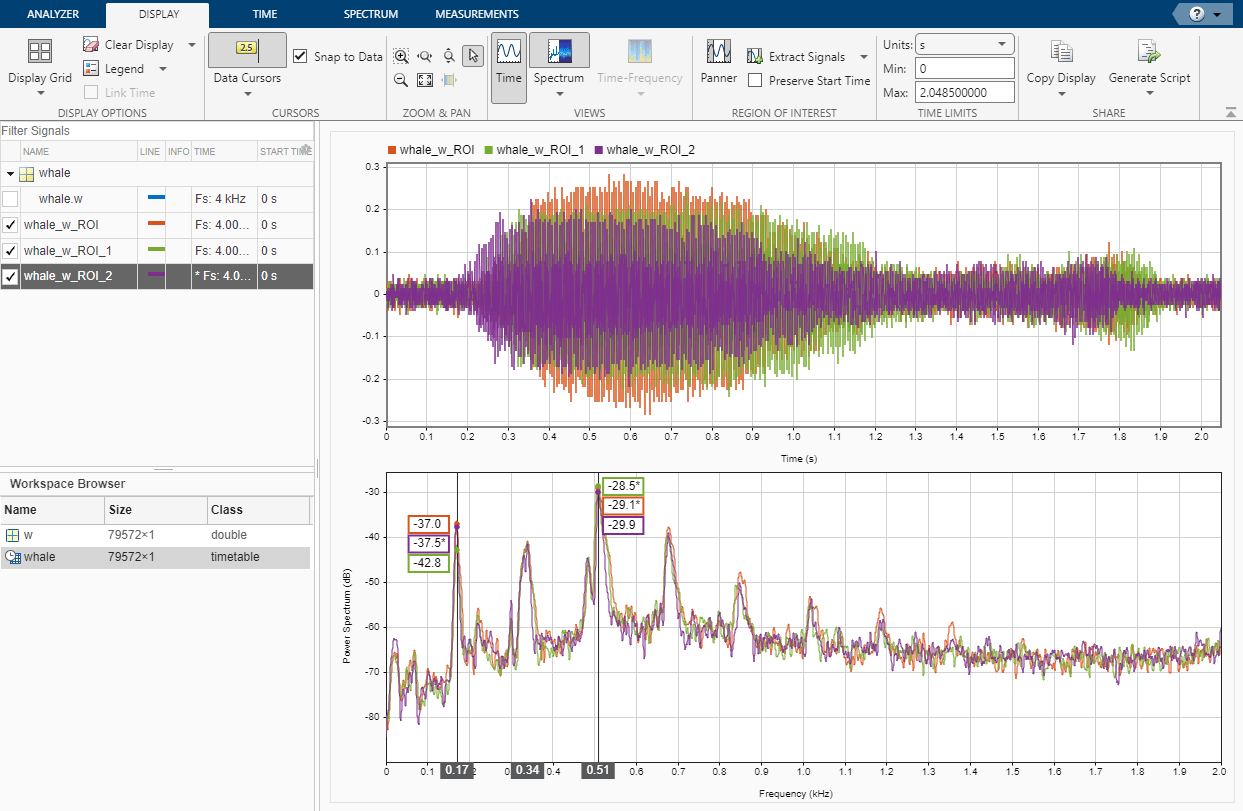
Periodogram, Welch, and Lomb-Scargle PSD, coherence, transfer function, frequency reassignment
- Parametric Spectral Estimation
Burg, Yule-Walker, covariance, and modified covariance methods
- Subspace Methods
Frequency and pseudospectrum estimates, multiple signal classification (MUSIC), root MUSIC
- Windows
Hamming, Blackman, Bartlett, Chebyshev, Taylor, Kaiser