afterAll
Run function after all functions finish running in the background
Description
B = afterAll(A,fcn,n)Future object B and runs the
function fcn automatically after all elements in the
Future array A finish.
MATLAB® runs the function fcn using the concatenated
outputs from each element in A. The outputs
Y1,...,Ym from each Future object are
concatenated vertically, in linear index order. For example, if
A is a two-element Future vector with
outputs y1 and y2 from the first and second
Future objects respectively, MATLAB runs fcn([y1; y2]) after all elements in
A finish.
If the Future array A has
M elements, MATLAB runs the function only once. When the scheduled function
fcn finishes, the Future object
B finishes.
You create a Future object when:
You run a function in the background using
backgroundPool.You run a function on a parallel pool when you have Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
For more information about using
afterAllon a parallel pool, see Use afterEach and afterAll to Run Callback Functions (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
If any of the elements in A encounters an error,
afterAll finishes with an error.
Examples
Run Callback Function After All Functions Finish
This example shows how to automatically invoke functions on all of the combined outputs of your parfeval computations.
Preallocate an array of Future objects, then use parfeval to compute random vectors and retrieve one output. Specify backgroundPool as the first argument to run the function in the background. Repeat 10 times to schedule 10 parfeval computations.
f(1:10) = parallel.FevalFuture; for idx = 1:10 f(idx) = parfeval(backgroundPool,@rand,1,1000,1); end wait(f)
After all the Future objects finish, display the maximum element among all of those vectors.
The input argument to max is the concatenated output of all the Future objects. Specify the third argument to the afterAll function as 0 to return no outputs from the callback.
afterAll(f,@(r) fprintf("Maximum element is %1.4f\n",max(r)),0);Handle Errors After All Functions Run in the Background
This example shows how to use afterAll to handle errors from functions that run in the background.
When you call afterAll on Future objects that result in errors, by default, afterAll also errors. If you want to handle any errors in the preceding futures, for example, when you have a user interface that you want to update, you can use the PassFuture argument. When you set PassFuture to true, MATLAB passes the array of Future objects to the callback function. You can interact with the individual elements of the Future array, process the outputs, and handle any possible errors.
Send computations to the background using parfeval. Some of these computations deliberately result in errors.
N = 10; F(1:N) = parallel.FevalFuture; for idx = 1:2:N F(idx) = parfeval(backgroundPool,@rand,1,1); end for idx = 2:2:N F(idx) = parfeval(backgroundPool,@rand,1,0.1); end
If any of the elements in the preceding futures encounters an error, afterAll finishes with an error. In the code below, afterAll errors. Use the Error property of the afterAll future a to view the error.
a = afterAll(F,@mean,1); wait(a) a.Error
ans =
MException with properties:
identifier: 'MATLAB:parallel:future:PrecedingExecutionErrors'
message: 'The preceding futures with IDs: 90,91,92,93,94 resulted in an error.'
cause: {5×1 cell}
stack: [0×1 struct]
Correction: []
To handle the elements in the preceding futures that have errors, write a callback function that takes in the future array as an input argument. The displayRunSummary helper function determine which futures completed successfully using the Error property and fetches their outputs. It then calculates the mean of the completed runs and displays this information in a user interface, including a table showing the completion status of each computation.
a2 = afterAll(F,@displayRunSummary,0,PassFuture=true);
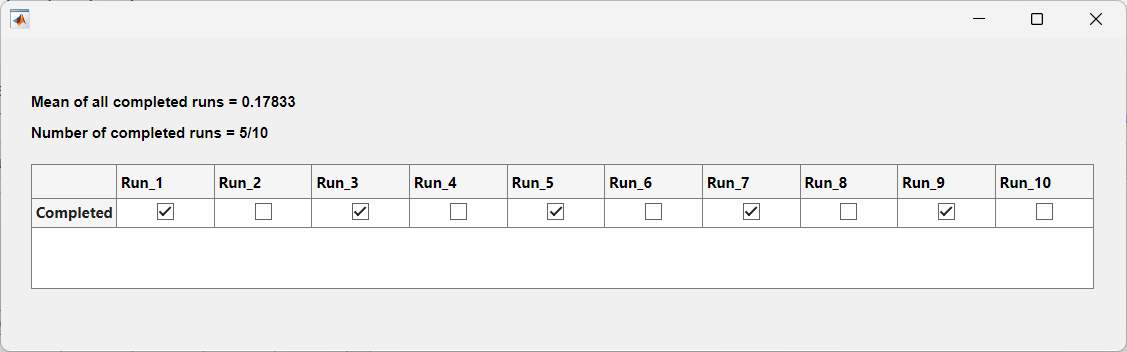
function displayRunSummary(F) N = numel(F); output = zeros(N,1); for idx = 1:N f = F(idx); field = strcat("Run_",num2str(idx)); results.(field) = isempty(f.Error); if isempty(f.Error) output(idx) = fetchOutputs(f); end end meanAll = mean(output,"omitmissing"); fig = uifigure('Position',[100 100 900 250]); runText = strcat("Number of completed runs = ", ... num2str(nnz(output)),"/",num2str(numel(output))); uilabel(fig,Text=runText,FontWeight="bold",Position=[25 125 700 100]); meanText = strcat("Mean of all completed runs = ",num2str(meanAll)); uilabel(fig,Text=meanText,FontWeight="bold",Position=[25 150 700 100]); t = struct2table(results); t.Properties.RowNames = "Completed"; uitable(fig,Position=[25 50 850 100],Data=t); end
Update Wait Bar While Functions Run in the Background
This example shows how to use afterEach to update a wait bar with the progress of functions running in the background.
Create a wait bar, w.
w = waitbar(0,'Please wait ...');
Set the number of iterations for your for-loop, N. Store the current number of completed iterations, 0, and the total number of iterations, N, in the UserData property of the wait bar.
N =  20;
w.UserData = [0 N];
20;
w.UserData = [0 N];Run a for-loop with N iterations. In each iteration, use parfeval and backgroundPool to run pause in the background for a random number of seconds. Store each Future object in an array.
for i = 1:N delay = rand; f(i) = parfeval(backgroundPool,@pause,0,delay); end
Use the helper function updateWaitbar to update the waitbar after each Future finishes.
afterEach(f,@(~)updateWaitbar(w),0);
Use delete to close the wait bar after all the Future objects finish.
afterAll(f,@(~)delete(w),0);
Define Helper Function
Define the helper function updateWaitbar. The function increments the first element of the UserData property, then uses the vector to calculate the progress.
function updateWaitbar(w) % Update a waitbar using the UserData property. % Check if the waitbar is a reference to a deleted object if isvalid(w) % Increment the number of completed iterations w.UserData(1) = w.UserData(1) + 1; % Calculate the progress progress = w.UserData(1) / w.UserData(2); % Update the waitbar waitbar(progress,w); end end
Input Arguments
A — Input Future
parallel.Future scalar | parallel.Future array
Input Future object, specified as a parallel.Future scalar or array.
MATLAB runs the function fcn after all elements
in A finish.
By default,
PassFutureisfalse, and MATLAB runs the callback function using the concatenated outputsY1,...,Ymfrom eachFutureelement inA. The outputsY1,...,Ymfrom eachFutureobject are concatenated vertically, in linear index order. For example, ifAis a two-elementFuturevector with outputsy1andy2from the first and secondFutureobjects respectively, MATLAB runsfcn([y1; y2])after all elements inAfinish.If any of the elements in
Aencounters an error,afterAllfinishes with an error.If you specify
PassFutureastrue, MATLAB runs the callback function asfcn(A).If any of the elements in
Aencounters an error,afterAlldoes not finish with an error.
If the Future array has M elements,
MATLAB runs the function M times. When the
scheduled function fcn finishes, the
Future object B finishes.
Example: A =
parfeval(backgroundPool,@magic,1,3);
fcn — Callback function to run
function handle
Callback function to run, specified as a function handle.
Example: fcn = @magic
n — Number of output arguments
nonnegative integer scalar
Number of output arguments, specified as a nonnegative integer scalar.
If you specify
PassFutureastrue,nis the number of output arguments expected from runningfcn(A)using theFuturearrayA.Otherwise,
nis the number of output arguments expected from runningfcn(Y1,...,Ym)using the vertically concatenated outputsY1,...,Ymfrom each elementAjin theFuturearrayA.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
PassFuture — Pass Future array A to callback function
falseor 0 (default) | true or 1
Pass the Future array A to callback
function, specified as true or false.
By default
PassFutureis false and MATLAB runs the functionfcnusing the concatenated outputs from each element inA. The outputsY1,...,Ymfrom eachFutureobject are concatenated vertically, in linear index order. For example, ifAis a two-elementFuturevector with outputsy1andy2from the first and secondFutureobjects respectively, MATLAB runsfcn([y1; y2])after all elements inAfinish.If any of the elements in
Aencounters an error,afterAllfinishes with an error.If you specify
PassFutureastrue, MATLAB runsfcn(A)after allFutureelements inAfinishes, instead of concatenating the outputs of theFutureelements inA.If any of the elements in
Aencounters an error,afterAlldoes not finish with an error.
Data Types: logical
Output Arguments
B — Output Future
parallel.Future object
Output Future object, returned as a
parallel.Future object.
Use
fetchOutputsto retrieve results fromB.Use
afterEachorafterAllto run a function whenBcompletes.
When you set PassFuture, you change the
Error property of B if
afterAll does not result in an error:
By default,
PassFutureisfalse, and if any of the elements inAencounters an error,afterAllfinishes with an error. TheErrorproperty ofBis anMExceptionobject.To find the cause of the error, use the
causeproperty ofB.Error.If
PassFutureistrue, and any of the elements inAencounters an error,afterAlldoes not finish with an error. TheErrorproperty ofBis an emptyMExceptionobject.
If afterAll results in an error, the
Error property of B is an
MException object.
Version History
Introduced in R2018a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.

Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other bat365 country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- New Zealand (English)
- 中国
- 日本Japanese (日本語)
- 한국Korean (한국어)