GPU Code Generation for Lane Detection in Simulink
This example shows how to generate CUDA® code for a Simulink® model that can detect and output lane marker boundaries on an image. This example takes RGB image as an input and uses the imresize, rgb2gray, ordfilt2 (Image Processing Toolbox), hough (Image Processing Toolbox), houghpeaks (Image Processing Toolbox), and houghlines (Image Processing Toolbox) functions that are part of Image Processing Toolbox™ to detect lane markings. This example closely follows Lane Detection on the GPU by Using the houghlines Function.
This example illustrates the following concepts:
Model a lane detection application in Simulink by using image processing functions.
Configure the model for GPU code generation.
Generate a CUDA executable for the Simulink model.
Third-Party Prerequisites
Required
This example generates CUDA MEX and has the following third-party requirements.
CUDA enabled NVIDIA® GPU and compatible driver.
Optional
For non-MEX builds such as static, dynamic libraries or executables, this example has the following additional requirements.
NVIDIA toolkit.
Environment variables for the compilers and libraries. For more information, see Third-Party Hardware and Setting Up the Prerequisite Products.
Verify GPU Environment
To verify that the compilers and libraries necessary for running this example are set up correctly, use the coder.checkGpuInstall function.
envCfg = coder.gpuEnvConfig('host');
envCfg.BasicCodegen = 1;
envCfg.Quiet = 1;
coder.checkGpuInstall(envCfg);
Lane Detection using houghlines Simulink Model
The Simulink model for lane detection is shown.
open_system('lane_detection');
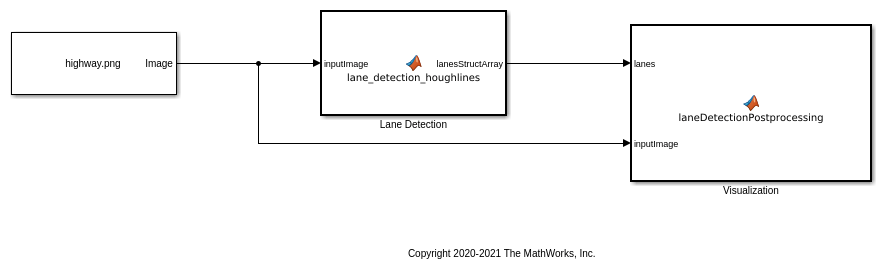
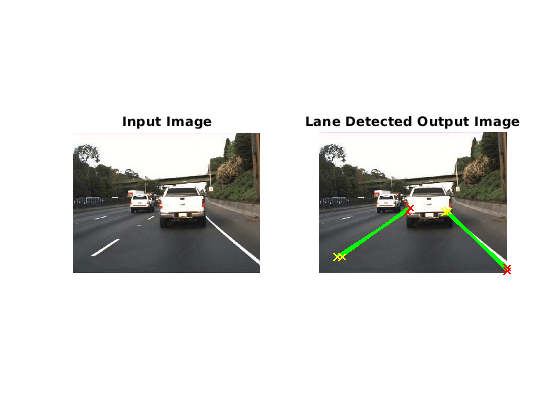
The Lane Detection subsystem contains a MATLAB Function block that takes an intensity image as input and provides detected lanes as output. This function is based on the lane detection algorithm implementation using houghlines as described in Lane Detection on the GPU by Using the houghlines Function example. When the model runs, the Visualization block displays the lane detected output image.
Run the Simulation
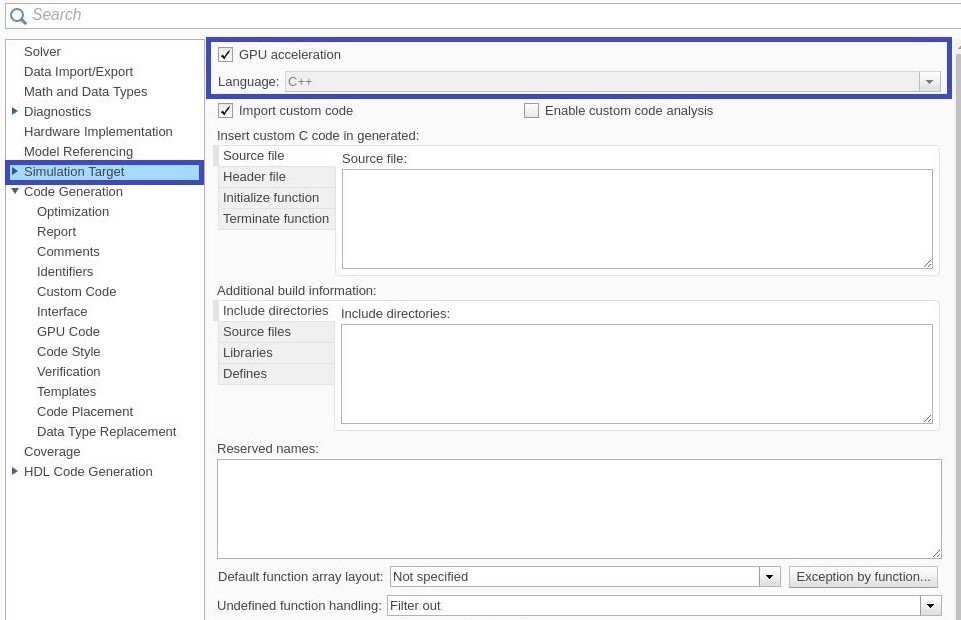
Open Configuration Parameters dialog box.
In Simulation Target pane, select GPU acceleration.
Run the simulation in Normal mode.
set_param('lane_detection', 'SimulationMode', 'Normal'); sim('lane_detection');
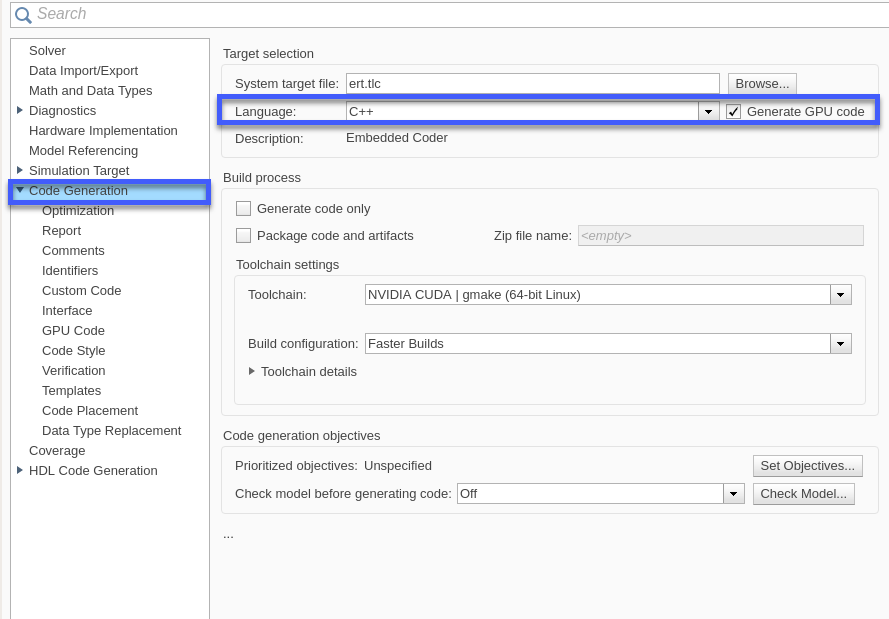
Generate and Build the Simulink Model
In Code Generation pane, select the Language as C++ and enable Generate GPU code.
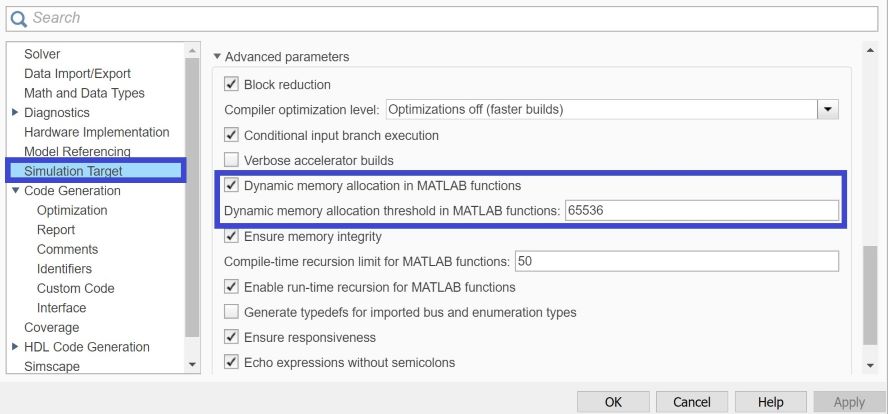
Open Simulation Target pane. In the Advanced parameters, enable Dynamic memory allocation threshold in MATLAB functions. For more information, see Dynamic memory allocation in MATLAB functions (Simulink)
Open Code Generation > GPU Code pane. In the subcategory Libraries, enable cuBLAS, cuSOLVER and cuFFT.
Generate and build the Simulink model on the host GPU by using the slbuild command. The code generator places the files in a build folder, a subfolder named lane_detection_ert_rtw under your current working folder.
status = evalc("slbuild('lane_detection')");
Cleanup
Close the Simulink model.
close_system('lane_detection');
See Also
Functions
open_system(Simulink) |load_system(Simulink) |save_system(Simulink) |close_system(Simulink) |bdclose(Simulink) |get_param(Simulink) |set_param(Simulink) |sim(Simulink) |slbuild(Simulink)
