laneType
Create road lane type object
Description
lt = laneType(type)Type,
Color, and Strength to define different lane types
for a road.
You can use this object to create driving scenarios with roads that have driving lanes, border lanes, restricted lanes, shoulder lanes, and parking lanes. You can also load this scenario into the Driving Scenario Designer app.
For details on the steps involved in using laneType function with
the drivingScenario object and the Driving Scenario
Designer app, see More About.
lt = laneType(type,Name,Value)
Examples
Add Roads That Have Different Lane Types to Driving Scenario
This example shows how to define lane types and simulate a driving scenario for a four-lane road that has different lane types.
Create a driving lane object with default property values.
drivingLane = laneType('Driving')drivingLane =
DrivingLaneType with properties:
Type: Driving
Color: [0.8000 0.8000 0.8000]
Strength: 1
Create a parking lane type object. Specify the color and the strength property values.
parkingLane = laneType('Parking','Color',[1 0 0],'Strength',0.1)
parkingLane =
ParkingLaneType with properties:
Type: Parking
Color: [1 0 0]
Strength: 0.1000
Create a three-element, heterogeneous lane type array by concatenating the driving and the parking lane type objects. The lane type array contains lane types for a four-lane road.
lt = [parkingLane drivingLane drivingLane parkingLane];
Create lane specification for a four-lane road. Add the lane type array to the lane specification.
ls = lanespec([2 2],'Type',lt);Create a driving scenario object. Add the four-lane road with lane specifications ls to the driving scenario.
scenario = drivingScenario;
roadCenters = [0 0 0;40 0 0];
road(scenario,roadCenters,'Lanes',ls)ans =
Road with properties:
Name: ""
RoadID: 1
RoadCenters: [2x3 double]
RoadWidth: 14.5500
BankAngle: [2x1 double]
Heading: [2x1 double]
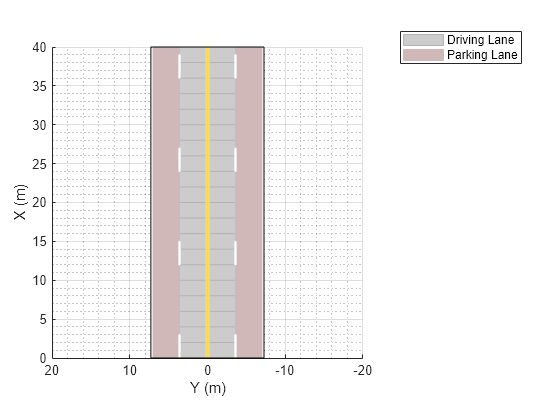
Plot the scenario. The scenario contains the four-lane road that has two parking lanes and two driving lanes.
plot(scenario) legend('Driving Lane','Parking Lane')
Simulate Vehicles Traveling on Road That Has Multiple Lane Types
Create a heterogeneous lane type object array to define driving, shoulder, and border lane types for a four-lane road.
lt = [laneType('Shoulder') laneType('Driving') laneType('Driving') laneType('Border','Color',[0.5 0 1],'Strength',0.1)];
Display the lane type object array.
lt
lt=1×4 heterogeneous LaneType (ShoulderLaneType, DrivingLaneType, BorderLaneType) array with properties:
Type
Color
Strength
Inspect the property values.
c = [{lt.Type}' {lt.Color}' {lt.Strength}'];
cell2table(c,'VariableNames',{'Type','Color','Strength'})ans=4×3 table
Type Color Strength
________ ____________________ ________
Shoulder 0.59 0.59 0.59 1
Driving 0.8 0.8 0.8 1
Driving 0.8 0.8 0.8 1
Border 0.5 0 1 0.1
Pass the lane type object array as input to the lanespec function, and then create a lane specification object for the four-lane road.
lspec = lanespec([2 2],'Type',lt);Define the road centers.
roadCenters = [0 0 0; 40 0 0];
To add roads, create a driving scenario object.
scenario = drivingScenario('StopTime',8);Add roads with the specified road centers and lane types to the driving scenario.
road(scenario,roadCenters,'Lanes',lspec);Add two vehicles to the scenario. Position the vehicles on the driving lane.
vehicle1 = vehicle(scenario,'ClassID',1,'Position',[5 2 0]); vehicle2 = vehicle(scenario,'ClassID',1,'Position',[35 -2 0]);
Define the vehicle trajectories by using waypoints. Set the vehicle trajectory speeds.
waypoints1 = [5 2;10 2;20 2;25 2;30 5;34 5.5]; smoothTrajectory(vehicle1,waypoints1,10) waypoints2 = [35 -2;20 -2;10 -2;5 -2]; smoothTrajectory(vehicle2,waypoints2,5)
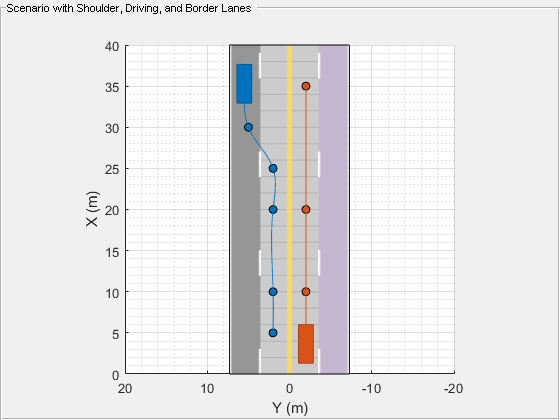
Plot the scenario. To advance the simulation one time step at a time, call the advance function in a loop. Pause every 0.01 second to observe the motion of the vehicles on the plot. The first vehicle travels along the trajectory in the driving lane. It drifts to the shoulder lane for emergency stopping.
% Create a custom figure window and define an axes object fig = figure; movegui(fig,'center'); hView = uipanel(fig,'Position',[0 0 1 1],'Title','Scenario with Shoulder, Driving, and Border Lanes'); hPlt = axes(hView); % Plot the generated driving scenario along with the waypoints. plot(scenario,'Waypoints','on','Parent',hPlt); while advance(scenario) pause(0.01) end
Input Arguments
type — Lane type
'Driving' | 'Border' | 'Restricted' | 'Shoulder' | 'Parking'
Lane type, specified as 'Driving', 'Border',
'Restricted', 'Shoulder', or
'Parking'.
| Lane Type | Description |
'Driving' | Lanes for driving |
'Border' | Lanes at the road borders |
'Restricted' | Lanes reserved for high occupancy vehicles |
'Shoulder' | Lanes reserved for emergency stopping |
'Parking' | Lanes alongside driving lanes, intended for parking vehicles |
Note
The lane type input sets the Type property of the output lane
type object.
Data Types: char | string
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: laneType('Driving','Color','r')
Color — Lane color
RGB triplet | color name
Lane color, specified as the comma-separated pair consisting of
'Color' and an RGB triplet or color name.
Specify the RGB triplet as a three-element row vector containing the intensities
of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the
range [0,1], for example, [0.4 0.6 0.7]. This
table lists the RGB triplet values that specify the default colors for different lane types.
| Lane Type | RGB Triplet (Default values) | Appearance |
'Driving' | [0.8 0.8 0.8] |
|
'Border' | [0.72 0.72 0.72] |
|
'Restricted' | [0.59 0.56 0.62] |
|
'Shoulder' | [0.59 0.59 0.59] |
|
'Parking' | [0.28 0.28 0.28] |
|
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options and the equivalent RGB triplet values.
| Color Name | RGB Triplet | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
'red' | [1 0 0] |
|
'green' | [0 1 0] |
|
'blue' | [0 0 1] |
|
'cyan'
| [0 1 1] |
|
'magenta' | [1 0 1] |
|
'yellow' | [0.98 0.86 0.36] |
|
'black' | [0 0 0] |
|
'white' | [1 1 1] |
|
Note
Use the lane color name-value pair to set the Color property
of the output lane type object.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | char | string
Strength — Strength of lane color
1 (default) | real scalar in the range [0, 1]
Strength of lane color, specified as a comma-separated pair consisting of
'Strength' and a real scalar in the range [0, 1]. A value of
0 desaturates the color and the lane color appears gray. A value
of 1 fully saturates the color and the lane color is the pure
color. You can vary the strength value to modify the level of saturation.
Note
Use the strength of lane color name-value pair to set the
Strength property of the lane type object.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Output Arguments
lt — Lane type
DrivingLaneType object | BorderLaneType object | RestrictedLaneType object | ShoulderLaneType object | ParkingLaneType object
Lane type, returned as a
DrivingLaneTypeobjectBorderLaneTypeobjectRestrictedLaneTypeobjectShoulderLaneTypeobjectParkingLaneTypeobject
The returned object lt depends on the value of the input
type.
type | lt |
'Driving' | DrivingLaneType object |
'Border' | BorderLaneType object |
'Restricted' | RestrictedLaneType object |
'Shoulder' | ShoulderLaneType object |
'Parking' | ParkingLaneType object |
You can create a heterogeneous LaneType array by concatenating
these different lane type objects.
More About
Create Driving Scenario With Roads That Have Multiple Lane Types
You can add roads that have multiple lane types to the driving scenario by following these steps
Create an empty
drivingScenarioobject.Create a lane type object that defines different lane types on the road by using
laneType.Use lane type object as input to the
lanespecobject and define lane specifications for the road.Use
lanespecobject as input to theroadfunction and add roads that have the specified lane types to the driving scenario.
You can use the plot function to visualize the driving
scenario.
You can also import a driving scenario containing roads that have
different lane types into the Driving Scenario
Designer app. To import a drivingScenario object named
scenario into the app, use the syntax
drivingScenarioDesigner(scenario). In
the
scenarios,
you can:
Add or edit the road centers.
Add actors and define actor trajectories.
Mount sensors on the ego vehicle and simulate detection of actors and lane boundaries.
Note
Editing the lane parameters resets all the lanes in the imported road to lane type
'Driving' with the default property values.
Version History
Introduced in R2019b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.

Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other bat365 country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- New Zealand (English)
- 中国
- 日本Japanese (日本語)
- 한국Korean (한국어)