i2cdev
Connection to device on Raspberry Pi hardware
Description
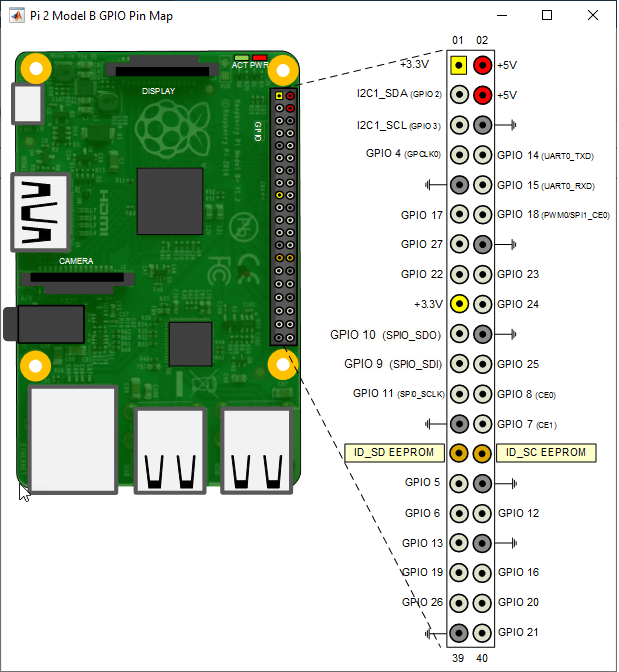
This object represents a connection from the MATLAB® software to the device on Raspberry Pi® hardware I2C bus. Attach an I2C device to the appropriate pins on the Raspberry Pi hardware. To interact with the I2C device, use this object with the functions listed in Object Functions.
Creation
Description
Input Arguments
Properties
Object Functions
read | Read data from I2C device |
write | Write data to I2C device |
readRegister | Read from register on I2C device |
writeRegister | Write to register on I2C device |