Triangle Wave Generator
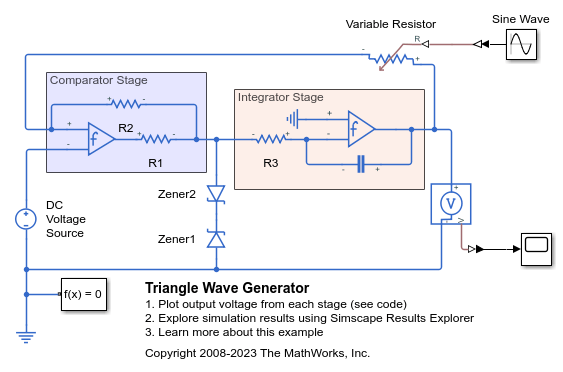
This example shows an implementation of a triangle wave generator circuit using two op-amps. The first stage of the circuit is a comparator constructed from an op-amp. The output of the comparator is limited to about plus or minus 5 volts by the two zener diodes. The limits imposed by the zener diodes result in a square wave.
The second stage of the circuit is an integrator. Integrating the square wave creates a triangle wave. The Sine Wave block modulates the waveform amplitude via the Variable Resistor block, and the DC Voltage Source can be used to add a DC offset. See the Example - Modeling a Triangle Wave Generator section of the Simscape™ Electrical™ User Guide for more information on how to construct this model using the Simscape and Simscape Electrical block libraries.
The two Band-Limited Op-Amp blocks are parameterized based on an LM7301 device. The datasheet gives the gain as 97dB which is equivalent to a gain of 10^(97/20)=7.1e4. Input resistance is given as 39e6 ohms, and slew rate as 1.25V per microsecond. Bandwidth is given as 4MHz. No value is given for the output resistance, so this is set to zero. In practice the output resistance will be small compared to output series 1000 ohm resistor in this circuit.
Model
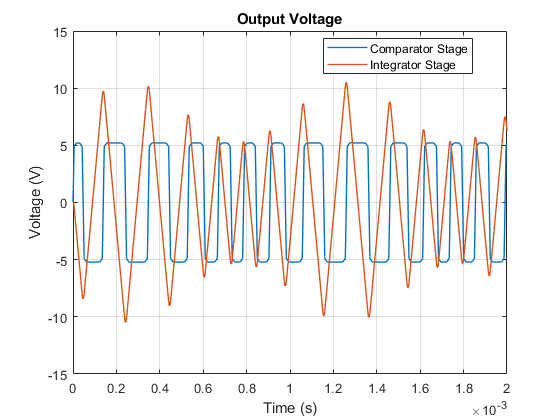
Simulation Results from Simscape Logging
The plot below shows the output voltage of each stage for the triangle wave circuit. The comparator with limits imposed by the zener diodes creates a square wave. Integrating the square wave produces a triangle wave.
Results from Real-Time Simulation
This example has been tested on a Speedgoat Performance real-time target machine with an Intel® 3.5 GHz i7 multi-core CPU. This model can run in real time with a step size of 40 microseconds.
