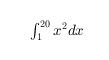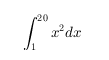TextArrow Properties
Text arrow appearance and behavior
TextArrow properties control the appearance
and behavior of a TextArrow object. By changing
property values, you can modify certain aspects of the text arrow. Use dot notation to
query and set properties.
ta = annotation("textarrow");
s = ta.FontSize;
ta.FontSize = 12;Text
String — Text to display
'' (default) | character vector | cell array of character vectors | string array | categorical array | numeric value
Text to display, specified as a character vector, cell array of character vectors, string array, categorical array, or numeric value. Specify a value according to how you want the text to appear. This table lists the most common situations.
| Appearance of Text | Description of Value | Example |
|---|---|---|
| One line of text | Character vector or 1-by-1 string array. | str = 'My Text'str = "My Text" |
| Multiple lines of text | Cell array of character vectors or a string array. | str = {'First line','Second line'};str = ["First line", "Second line"]; |
| Text that includes a numeric variable | Array that includes the number converted to a
char array. Use num2str to convert
the value. |
x = 42;
str = ['The value is ',num2str(x)]; |
| Text that includes special characters such as Greek letters or mathematical symbols | Array that includes TeX markup. For a list of supported markup,
see the Interpreter property. |
str = 'x ranges from 0 to 2\pi' |
Note
The words
default,factory, andremoveare reserved words that do not appear in text when quoted as normal characters. To display any of these words individually, precede them with a backslash, such as'\default'or'\remove'.If you specify this property as a categorical array, MATLAB® uses the values in the array, not the categories.
If you specify text that contains only a numeric value, the value is converted using
sprintf('%g',value). For example,12345678displays as1.23457e+07.
TextRotation — Text rotation angle in degrees
0 (default) | scalar numeric value
Text rotation angle in degrees, specified as a scalar numeric value. Set this property to a positive value to rotate the text counterclockwise. Angles are absolute and not relative to previous rotations. A rotation of 0 degrees is always horizontal.
Example: 90
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical
TextColor — Text color
[0 0 0]
(default) | RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | "r" | "g" | "b" | ...
Text color, specified as a three-element RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color
code, a color name, or a short name. The default value of [0 0
0] corresponds to black.
Note
Setting the Color property changes the
TextColor property to the same value, unless you
explicitly set the TextColor property.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable | No color |
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots.
| RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
[0 0.4470 0.7410] | "#0072BD" |
|
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980] | "#D95319" |
|
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250] | "#EDB120" |
|
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560] | "#7E2F8E" |
|
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880] | "#77AC30" |
|
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330] | "#4DBEEE" |
|
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840] | "#A2142F" |
|
Example: "blue"
Example: [0 0 1]
Example: "#0000FF"
TextEdgeColor — Color of text box outline
"none" (default) | RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | "r" | "g" | "b" | ...
Color of text box outline, specified as a three-element RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable | No color |
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots.
| RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
[0 0.4470 0.7410] | "#0072BD" |
|
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980] | "#D95319" |
|
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250] | "#EDB120" |
|
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560] | "#7E2F8E" |
|
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880] | "#77AC30" |
|
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330] | "#4DBEEE" |
|
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840] | "#A2142F" |
|
Example: "blue"
Example: [0 0 1]
Example: "#0000FF"
TextBackgroundColor — Color of text box background
"none" (default) | RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | "r" | "g" | "b" | ...
Color of text box background, specified as an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable | No color |
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots.
| RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
[0 0.4470 0.7410] | "#0072BD" |
|
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980] | "#D95319" |
|
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250] | "#EDB120" |
|
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560] | "#7E2F8E" |
|
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880] | "#77AC30" |
|
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330] | "#4DBEEE" |
|
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840] | "#A2142F" |
|
Example: "blue"
Example: [0 0 1]
Example: "#0000FF"
TextLineWidth — Width of text box outline
0.5 (default) | scalar numeric value
Width of text box outline, specified as a scalar numeric value in point
units. One point equals 1/72 inch.
Example: 1.5
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
TextMargin — Space around text within text box
2 (default) | scalar numeric value
Space around the text within the text box, specified as a scalar numeric value in pixel units.
Example: 10
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical
Interpreter — Text interpreter
'tex' (default) | 'latex' | 'none'
Text interpreter, specified as one of these values:
'tex'— Interpret characters using a subset of TeX markup.'latex'— Interpret characters using LaTeX markup.'none'— Display literal characters.
TeX Markup
By default, MATLAB supports a subset of TeX markup. Use TeX markup to add superscripts and subscripts, modify the font type and color, and include special characters in the text.
Modifiers remain in effect until the end of the text.
Superscripts and subscripts are an exception because they modify only the next character or the
characters within the curly braces. When you set the interpreter to 'tex',
the supported modifiers are as follows.
| Modifier | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
^{ } | Superscript | 'text^{superscript}' |
_{ } | Subscript | 'text_{subscript}' |
\bf | Bold font | '\bf text' |
\it | Italic font | '\it text' |
\sl | Oblique font (usually the same as italic font) | '\sl text' |
\rm | Normal font | '\rm text' |
\fontname{ | Font name — Replace
| '\fontname{Courier} text' |
\fontsize{ | Font size —Replace
| '\fontsize{15} text' |
\color{ | Font color — Replace
red, green,
yellow, magenta,
blue, black,
white, gray,
darkGreen, orange, or
lightBlue. | '\color{magenta} text' |
\color[rgb]{specifier} | Custom font color — Replace
| '\color[rgb]{0,0.5,0.5} text' |
This table lists the supported special characters for the
'tex' interpreter.
| Character Sequence | Symbol | Character Sequence | Symbol | Character Sequence | Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α |
| υ |
| ~ |
| ∠ |
| ϕ |
| ≤ |
|
|
| χ |
| ∞ |
| β |
| ψ |
| ♣ |
| γ |
| ω |
| ♦ |
| δ |
| Γ |
| ♥ |
| ϵ |
| Δ |
| ♠ |
| ζ |
| Θ |
| ↔ |
| η |
| Λ |
| ← |
| θ |
| Ξ |
| ⇐ |
| ϑ |
| Π |
| ↑ |
| ι |
| Σ |
| → |
| κ |
| ϒ |
| ⇒ |
| λ |
| Φ |
| ↓ |
| µ |
| Ψ |
| º |
| ν |
| Ω |
| ± |
| ξ |
| ∀ |
| ≥ |
| π |
| ∃ |
| ∝ |
| ρ |
| ∍ |
| ∂ |
| σ |
| ≅ |
| • |
| ς |
| ≈ |
| ÷ |
| τ |
| ℜ |
| ≠ |
| ≡ |
| ⊕ |
| ℵ |
| ℑ |
| ∪ |
| ℘ |
| ⊗ |
| ⊆ |
| ∅ |
| ∩ |
| ∈ |
| ⊇ |
| ⊃ |
| ⌈ |
| ⊂ |
| ∫ |
| · |
| ο |
| ⌋ |
| ¬ |
| ∇ |
| ⌊ |
| x |
| ... |
| ⊥ |
| √ |
| ´ |
| ∧ |
| ϖ |
| ∅ |
| ⌉ |
| 〉 |
| | |
| ∨ |
| 〈 |
| © |
LaTeX Markup
To use LaTeX markup, set the interpreter to 'latex'. For inline
mode, surround the markup with single dollar signs ($). For
display mode, surround the markup with double dollar signs
($$).
| LaTeX Mode | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Inline |
'$\int_1^{20} x^2 dx$' |
|
| Display |
'$$\int_1^{20} x^2 dx$$' |
|
The displayed text uses the default LaTeX font style. The
FontName, FontWeight, and
FontAngle properties do not have an effect. To change the
font style, use LaTeX markup.
The maximum size of the text that you can use with the LaTeX interpreter is 1200 characters. For multiline text, this reduces by about 10 characters per line.
For examples that use TeX and LaTeX, see Greek Letters and Special Characters in Chart Text. For more information about the LaTeX system, see The LaTeX Project website at https://www.latex-project.org/.
Font
FontName — Font name
supported font name | "FixedWidth"
Font name, specified as a supported font name or "FixedWidth". To display
and print text properly, you must choose a font that your system supports. The default
font depends on your operating system and locale.
To use a fixed-width font that looks good in any locale, use "FixedWidth".
The fixed-width font relies on the root FixedWidthFontName
property. Setting the root FixedWidthFontName property causes an
immediate update of the display to use the new font.
FontSize — Font size
scalar value greater than 0
Font size, specified as a scalar value greater than 0 in point units. The default font size
depends on the specific operating system and locale. One point equals 1/72 inch. To
change the font units, use the FontUnits property.
Example: 12
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical
FontWeight — Character thickness
'normal' (default) | 'bold'
Character thickness, specified as 'normal' or
'bold'.
MATLAB uses the FontWeight property to select a font from
those available on your system. Not all fonts have a bold weight. Therefore, specifying
a bold font weight can still result in the normal font weight.
FontAngle — Character slant
'normal' (default) | 'italic'
Character slant, specified as 'normal' or
'italic'.
Not all fonts have both font styles. Therefore, the italic font might look the same as the normal font.
FontUnits — Font size units
'points' (default) | 'inches' | 'centimeters' | 'normalized' | 'pixels'
Font size units, specified as one of the values in this table.
Units | Description |
|---|---|
'points' | Points. One point equals 1/72 inch. |
'inches' | Inches. |
'centimeters' | Centimeters. |
'normalized'
| Interpret font size as a fraction of the parent
container height, typically a figure. If you resize the
container, the font size modifies accordingly. For
example, if the FontSize is
0.1 in normalized units, then the
text is 1/10 of the container height. |
'pixels' |
Pixels. Starting in R2015b, distances in pixels are independent of your system resolution on Windows® and Macintosh systems:
On Linux® systems, the size of a pixel is determined by your system resolution. |
If you set both the font size and the font units in one function call, you
must set the FontUnits property first so that the axes
correctly interprets the specified font size.
Arrow
Color — Arrow color
[0 0 0]
(default) | RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | "r" | "g" | "b" | ...
Arrow color, specified as a three-element RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color
code, a color name, or a short name. The default value of [0 0
0] corresponds to black.
Note
Setting this property also changes the text color if you have not
explicitly set the text color using the TextColor
property.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable | No color |
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots.
| RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
[0 0.4470 0.7410] | "#0072BD" |
|
[0.8500 0.3250 0.0980] | "#D95319" |
|
[0.9290 0.6940 0.1250] | "#EDB120" |
|
[0.4940 0.1840 0.5560] | "#7E2F8E" |
|
[0.4660 0.6740 0.1880] | "#77AC30" |
|
[0.3010 0.7450 0.9330] | "#4DBEEE" |
|
[0.6350 0.0780 0.1840] | "#A2142F" |
|
Example: "blue"
Example: [0 0 1]
Example: "#0000FF"
LineStyle — Style of arrow stem
"-" (default) | "--" | ":" | "-." | "none"
Style of arrow stem, specified as one of the line styles listed in this table.
| Line Style | Description | Resulting Line |
|---|---|---|
"-" | Solid line |
|
"--" | Dashed line |
|
":" | Dotted line |
|
"-." | Dash-dotted line |
|
"none" | No line | No line |
LineWidth — Width of arrow stem
0.5 (default) | scalar numeric value
Width of arrow stem, specified as a scalar numeric value greater than zero
in point units. One point equals 1/72 inch. The default
value is 0.5 points.
Example: 0.75
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
HeadStyle — Style of arrowhead
"vback2" (default) | "plain" | "ellipse" | "vback1" | "vback3" | "cback1" | ...
Style of the arrowhead, specified as one of the head style options in this table.
| Style | Result | Style | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
"plain" |
| "fourstar" |
|
"ellipse" |
| "rectangle" |
|
"vback1" |
| "diamond" |
|
"vback2" (default) |
| "rose" |
|
"vback3" |
| "hypocycloid" |
|
"cback1" |
| "astroid" |
|
"cback2" |
| "deltoid" |
|
"cback3" |
| "none" | No arrowhead |
HeadLength — Length of arrowhead
10 (default) | scalar numeric value
Length of the arrowhead, specified as a scalar numeric value in point
units. One point equals 1/72 inch.
Example: 15
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical
HeadWidth — Width of arrowhead
10 (default) | scalar numeric value
Width of the arrowhead, specified as a scalar numeric value in point
units. One point equals 1/72 inch.
Example: 15
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical
Position
X — Beginning and ending x-coordinates
[0.3 0.4] (default) | two-element vector
Beginning and ending x-coordinates for the arrow,
specified as a two-element vector of the form [x_begin
x_end].
By default, the units are normalized to the figure. The lower-left corner
of the figure maps to (0,0), and the upper-right corner
maps to (1,1). To change the units, use the
Units property.
Example: [0.2 0.3]
Y — Beginning and ending y-coordinates
[0.3 0.4] (default) | two-element vector
Beginning and ending y-coordinates for the arrow,
specified as a two-element vector of the form [y_begin
y_end].
By default, the units are normalized to the figure. The lower-left corner
of the figure maps to (0,0), and the upper-right corner
maps to (1,1). To change the units, use the
Units property.
Example: [0.2 0.3]
Position — Size and location
[0.3 0.3 0.1 0.1] (default) | four-element vector
Size and location, specified as a four-element vector of the form
[x_begin y_begin length height]. The first two
elements specify the coordinates of the beginning of the arrow. The second
two elements specify the length and height of the arrow. The text box
extends from the beginning of the arrow.
By default, the units are normalized to the figure. The lower-left corner
of the figure maps to (0,0), and the upper-right corner
maps to (1,1). To change the units, use the
Units property.
Example: [0.2 0.2 0.3 0.1]
Units — Position units
"normalized" (default) | "inches" | "centimeters" | "characters" | "points" | "pixels"
Position units, specified as one of the values in this table.
Units | Description |
|---|---|
"normalized" (default) | Normalized with respect to the figure, uipanel, or uitab that
contains the annotation. The lower-left corner of the container maps
to (0,0) and the upper-right corner maps to (1,1). |
"inches" | Inches. |
"centimeters" | Centimeters. |
"characters" |
Based on the default system font character size.
|
"points" | Points. One point equals 1/72 inch. |
"pixels" | Pixels. Starting in R2015b, distances in pixels are independent of your system resolution on Windows and Macintosh systems:
On Linux systems, the size of a pixel is determined by your system resolution. |
All units are measured from the lower-left corner of the figure window.
This property affects the Position property.
If you change the units, then it is good practice to return it to
the default value after completing your computation to prevent affecting
other functions that assume Units is set to the
default value.
If you specify the Position and Units properties
using name-value arguments when creating the object, then the order of specification
matters. If you want to define the position with particular units, then you must set the
Units property before the Position
property.
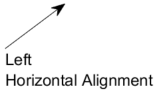
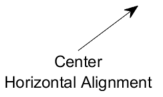
HorizontalAlignment — Horizontal alignment of text
'left' (default) | 'center' | 'right'
Horizontal alignment of the text, specified as one of the values in this table. This property is useful when aligning multiple lines of text.
| Value | Result |
|---|---|
'left'
|
|
'center' |
|
'right' |
|
VerticalAlignment — Vertical alignment of text with respect to arrow
'top' (default) | 'cap' | 'middle' | 'baseline' | 'bottom'
Vertical alignment of the text with respect to the end of the arrow,
specified as 'top', 'cap',
'middle', 'baseline', or
'bottom'.
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.

Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other bat365 country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- New Zealand (English)
- 中国
- 日本Japanese (日本語)
- 한국Korean (한국어)