sinh
Hyperbolic sine
Syntax
Description
Examples
Hyperbolic Sine of Vector
Create a vector and calculate the hyperbolic sine of each value.
X = [0 pi 2*pi 3*pi]; Y = sinh(X)
Y = 1×4
103 ×
0 0.0115 0.2677 6.1958
Graph of Hyperbolic Sine Function
Plot the hyperbolic sine over the domain .
x = -5:0.01:5;
y = sinh(x);
plot(x,y)
grid on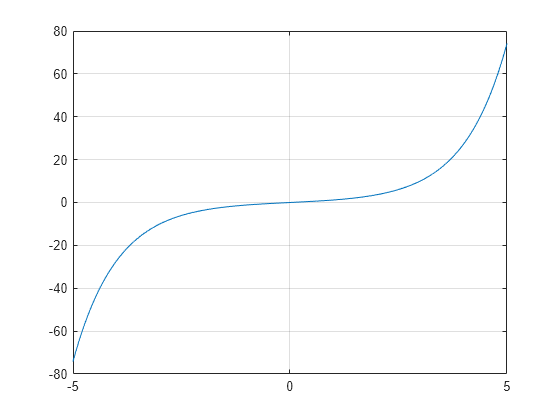
Plot Hyperbolic Sine and Exponential Functions
The hyperbolic sine satisfies the identity . In other words, is half the difference of the functions and . Verify this by plotting the functions.
Create a vector of values between -3 and 3 with a step of 0.25. Calculate and plot the values of sinh(x), exp(x), and exp(-x). As expected, the sinh curve is positive where exp(x) is large, and negative where exp(-x) is large.
x = -3:0.25:3; y1 = sinh(x); y2 = exp(x); y3 = exp(-x); plot(x,y1,x,y2,x,y3) grid on legend('sinh(x)','exp(x)','exp(-x)','Location','bestoutside')
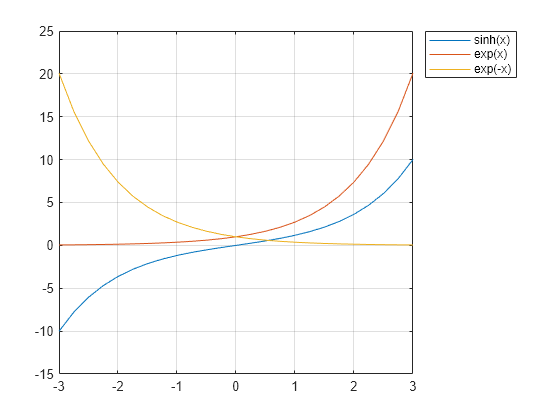
Input Arguments
X — Input angles in radians
scalar | vector | matrix | multidimensional array | table | timetable
Input angles in radians, specified as a scalar, vector, matrix, multidimensional array, table, or timetable.
Data Types: single | double | table | timetable
Complex Number Support: Yes
More About
Hyperbolic Sine
The hyperbolic sine of an angle x can be expressed in terms of exponential functions as
In terms of the traditional sine function with a complex argument, the identity is
Extended Capabilities
Tall Arrays
Calculate with arrays that have more rows than fit in memory.
The
sinh function fully supports tall arrays. For more information,
see Tall Arrays.
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
GPU Code Generation
Generate CUDA® code for NVIDIA® GPUs using GPU Coder™.
Thread-Based Environment
Run code in the background using MATLAB® backgroundPool or accelerate code with Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool.
This function fully supports thread-based environments. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions in Thread-Based Environment.
GPU Arrays
Accelerate code by running on a graphics processing unit (GPU) using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
The sinh function
fully supports GPU arrays. To run the function on a GPU, specify the input data as a gpuArray (Parallel Computing Toolbox). For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Distributed Arrays
Partition large arrays across the combined memory of your cluster using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
This function fully supports distributed arrays. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions with Distributed Arrays (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Version History
Introduced before R2006aR2023a: Perform calculations directly on tables and timetables
The sinh function can calculate on all variables within a table or
timetable without indexing to access those variables. All variables must have data types
that support the calculation. For more information, see Direct Calculations on Tables and Timetables.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.

Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other bat365 country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- New Zealand (English)
- 中国
- 日本Japanese (日本語)
- 한국Korean (한국어)