Generate Digit Images on NVIDIA GPU Using Variational Autoencoder
This example shows how to generate CUDA® MEX for a trained variational autoencoder (VAE) network. The example illustrates:
This example uses a pretrained decoder network based on the Train Variational Autoencoder (VAE) to Generate Images example from the Deep Learning Toolbox™. For more information, see Train Variational Autoencoder (VAE) to Generate Images (Deep Learning Toolbox).
Third-Party Prerequisites
Required
CUDA enabled NVIDIA® GPU and compatible driver.
Optional
For non-MEX builds such as static, dynamic libraries or executables, this example has the following additional requirements.
NVIDIA CUDA toolkit.
NVIDIA cuDNN library.
Environment variables for the compilers and libraries. For more information, see Third-Party Hardware and Setting Up the Prerequisite Products.
Verify GPU Environment
To verify that the compilers and libraries for running this example are set up correctly, use the coder.checkGpuInstall function.
envCfg = coder.gpuEnvConfig('host'); envCfg.DeepLibTarget = 'cudnn'; envCfg.DeepCodegen = 1; envCfg.Quiet = 1; coder.checkGpuInstall(envCfg);
Pretrained Variational Autoencoder Network
Autoencoders have two parts: the encoder and the decoder. The encoder takes an image input and outputs a compressed representation (the encoding), which is a vector of size latent_dim, equal to 20 in this example. The decoder takes the compressed representation, decodes it, and recreates the original image.
VAEs differ from regular autoencoders in that they do not use the encoding-decoding process to reconstruct an input. Instead, they impose a probability distribution on the latent space, and learn the distribution so that the distribution of outputs from the decoder matches that of the observed data. Then, they sample from this distribution to generate new data.
This example uses the decoder network trained in the Train Variational Autoencoder (VAE) to Generate Images example. To train the network yourself, see Train Variational Autoencoder (VAE) to Generate Images (Deep Learning Toolbox).
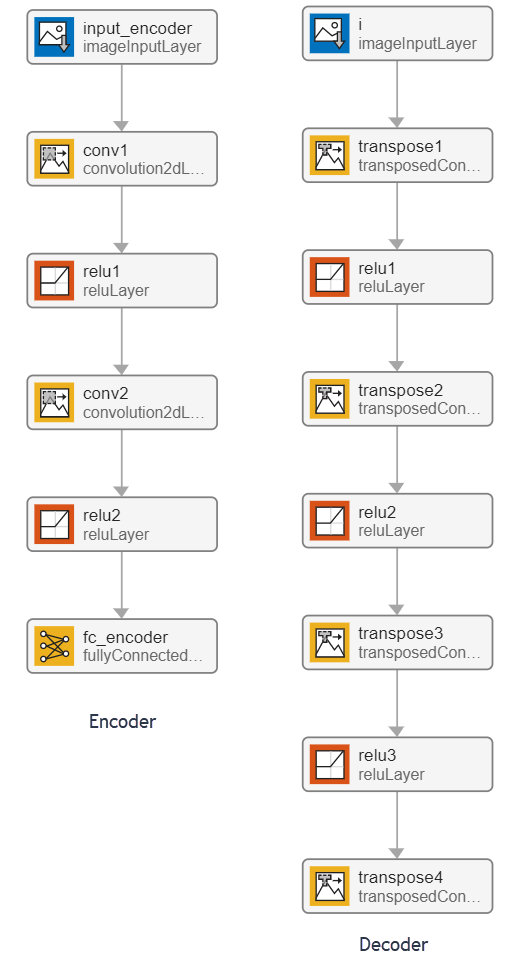
The generateVAE Entry-Point Function
The generateVAE entry-point function loads the dlnetwork object from the trainedDecoderVAENet MAT-file into a persistent variable and reuses the persistent object for subsequent prediction calls. It initializes a dlarray object containing 25 randomly generated encodings, passes them through the decoder network, and extracts the numeric data of the generated image from the deep learning array object.
type('generateVAE.m')function generatedImage = generateVAE(decoderNetFileName,latentDim,Environment) %#codegen
% Copyright 2020-2021 The bat365, Inc.
persistent decoderNet;
if isempty(decoderNet)
decoderNet = coder.loadDeepLearningNetwork(decoderNetFileName);
end
% Generate random noise
randomNoise = dlarray(randn(1,1,latentDim,25,'single'),'SSCB');
if coder.target('MATLAB') && strcmp(Environment,'gpu')
randomNoise = gpuArray(randomNoise);
end
% Generate new image from noise
generatedImage = sigmoid(predict(decoderNet,randomNoise));
% Extract numeric data from dlarray
generatedImage = extractdata(generatedImage);
end
Evaluate the Entry-Point Function
Evaluate the generateVAE entry-point function to generate digit images and plot the results.
latentDim = 20; matfile = 'trainedDecoderVAENet.mat'; Env = ''; figure() title("Generated samples of digits - MATLAB") generatedImageML = generateVAE(matfile, latentDim, Env); imshow(imtile(generatedImageML, "ThumbnailSize", [100,100]))

Generate CUDA MEX
To generate CUDA code for the generateVAE entry-point function, create a GPU code configuration object for a MEX target and set the target language to C++. Use the coder.DeepLearningConfig function to create a CuDNN deep learning configuration object and assign it to the DeepLearningConfig property of the GPU code configuration object.
Env = 'gpu'; cfg = coder.gpuConfig('mex'); cfg.TargetLang = 'C++'; cfg.DeepLearningConfig = coder.DeepLearningConfig('cudnn'); args = {coder.Constant(matfile), coder.Constant(latentDim), coder.Constant(Env)}; codegen -config cfg -args args generateVAE -report
Code generation successful: View report
To generate CUDA code for TensorRT target, create and use a TensorRT deep learning configuration object instead of the CuDNN configuration object.
Run the Generated MEX
Call the generated CUDA MEX and display the results.
figure() title("Generated samples of digits - GPU") generatedImageGPU = generateVAE_mex(matfile, latentDim, Env); imshow(imtile(generatedImageGPU, "ThumbnailSize", [100,100]))

The generateVAE entry-point function initializes the dlarray object with randomly generated encodings, passes them through the decoder network, and extracts the numeric data of the generated image from the deep learning array object. As a result, the image geenrated during MATLAB simulation is different from the image generated by the MEX function call.
See Also
Functions
Objects
coder.gpuConfig|coder.gpuEnvConfig|coder.CuDNNConfig|coder.TensorRTConfig|dlarray(Deep Learning Toolbox) |dlnetwork(Deep Learning Toolbox)
Related Examples
- Train Variational Autoencoder (VAE) to Generate Images (Deep Learning Toolbox)
More About
- Code Generation for dlarray
- dlarray Limitations for Code Generation
- Define Custom Training Loops, Loss Functions, and Networks (Deep Learning Toolbox)
- Train Network Using Custom Training Loop (Deep Learning Toolbox)
- Make Predictions Using dlnetwork Object (Deep Learning Toolbox)
