Memory Copy
Copy data from and to memory section
Description
Generated code for the Memory Copy block copies data from and to processor memory as configured by block parameters. When you use this block to copy an individual data element from a source to a destination, the block copies the element from the source, using the source data type, and then casts the data element to the specified destination data type.
Include as many instances of the Memory Copy block in a model as required to manipulate memory on a target processor. Each instance of the block works with one variable, address, or set of addresses provided to the block as input.
Specify the source and destination for a memory copy by using block parameters. You can use block parameters to control other aspects of a memory copy, such as:
Initialization for memory locations
Memory stride and offset during run time
Write operations to memory during program initialization, during program termination, and at every sample time
Insertion of custom ANSI® C source code before and after each memory copy read and write operation (for example, to lock and unlock registers before and after accessing them)
The Memory Copy block performs operations at three periods during program execution:
Initialization
Real-time operations
Termination
You can use block parameters to control when and how the block initializes memory, copies data or variables to and from memory, and terminates copy operations. The parameters enable you to turn on and off memory copy operations in the three periods independently.
Use the Memory Copy block and the Memory Allocate block to manipulate and allocate memory for custom device drivers, such as PCI bus drivers or codec-style drivers.
During simulation, the Memory Copy block does not perform an operation. The block output is not defined.
Ports
Input
src — Input data for copy operation
scalar | vector
The source data for the memory copy operation, specified as a scalar or vector.
Port Dependencies
To use this port as the source for the memory copy operation, set parameter
Copy from to Input port.
Data Types: single | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
&src — Address of input data for copy operation
scalar | vector
The memory address of source data for the copy operation, specified as a scalar or vector.
Port Dependencies
To use this port as the source for the memory copy operation, set parameter
Copy from to Specified address and
Specify address source to Input
port. The Copy Memory block converts input port
src to &src.
Data Types: single | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
src ofs — Offset for data read during copy operation
scalar | vector
Offset to use for data read during the copy operation, specified as a scalar or vector.
Port Dependencies
To create this port, select parameter Use offset when
reading and set Specify offset source to
Input port.
Data Types: single | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
&dst — Address of output data for copy operation
scalar | vector
The memory address to use as the data destination for the copy operation, specified as a scalar or vector.
Port Dependencies
To use this port as the destination for the memory copy operation, set parameter
Copy to to Specified address and
Specify address source to Input
port. The Copy Memory block converts output port
dst to input port &dst.
Data Types: single | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
dst ofs — Offset for data written during copy operation
scalar | vector
Offset to use for data write during the copy operation, specified as a scalar or vector.
Port Dependencies
To create this port, select parameter Use offset when
writing and set Specify offset source to
Input port.
Data Types: single | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Output
dst — Output data for copy operation
scalar | vector
The data copied, specified as a scalar or vector.
Port Dependencies
To use this port as the destination for the memory copy operation, set parameter
Copy to to Output port.
Data Types: single | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Parameters
Source
Specify the source sequential memory location for the copy operation. Specify the data type, size, and other attributes of the source variable.
Copy from — Input source for copy operation
Input port (default) | Specified address | Specified source code symbol
Specify the input source for the data read part of the copy operation. Choose from the sources listed in this table.
| Source of Data Read | Parameter Value to Specify |
|---|---|
src input port | Input port |
| Memory address | Specified address |
| Symbol (variable) in source code lookup table | Specified source code symbol |
Parameter Dependencies
If you select
Specified address, use Specify address source to specify the source of the memory address and Address to specify the address.If you select
Specified source code symbol, use Source code symbol to specify the symbol (variable) in the source code symbol table to copy.If you select
Specified addressorSpecified source code symbol, change Data type to a value other thanInherit from source(the default). If you do not make this change, you receive an error message indicating that the data type cannot be inherited because the input port does not exist.
Specify address source — Source of memory address for input data
Specify via dialog (default) | Input port
Specify the source of the memory address of the input source for the copy
operation. To specify a memory address for the source variable, select
Specify via dialog. That selection enables an
Address parameter that you use to specify the memory address.
To specify that the block get the address from the input port, select
Input port. When you select Input
port, the block input port label changes to
&src.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Copy from to
Specified address.If you select
Specify via dialog, this parameter enables the Address parameter, which you use to specify the address of the source variable.If you select
Specify via dialog, set Data type to a value other thanInherit from source(the default). If you do not make this change, you receive an error message indicating that the data type cannot be inherited because the input port does not exist.If you select
Inport port, specify a data type for the Data type parameter.
Address — Memory address of source data
hex2dec('00001000') (default) | memory address in decimal or hexadecimal form with a conversion to
decimal
Specify the memory address of the source data in decimal form or in hexadecimal
form with a conversion to decimal as shown by the default value
hex2dec('00001000').
This example converts Ox1000 to decimal form.
4096 = hex2dec('1000');For this example, you can specify the address as 4096 or
hex2dec('1000').
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Copy from to
Specified address and Specify address
source to Specify via dialog.
Source code symbol — Symbol in source code symbol table
myVariableSrc (default) | string | character vector
Specify the symbol (variable) in the source code symbol table to copy. The symbol that you specify must exist in the symbol table for your program. The block does not verify whether the symbol exists in the symbol table and whether you specify the symbol with valid syntax. Enter text that specifies the symbol exactly as it appears in your code.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Copy from to
Specified source code symbol.Set Data type to a value other than
Inherit from source(the default). If you do not make this change, you receive an error message indicating that the data type cannot be inherited because the input port does not exist.
Data type — Data type of data being copied
uint8 (default) | double | single | int8 | int16 | uint16 | int32 | uint32 | int64 | uint64 | boolean | Inherit from input port
Specify the data type of the source data being copied. To inherit the data type
from the src input port, select Inherit from input
port.
Data length — Number of data elements to copy
1 (default) | positive integer
Specify the number of elements to copy from the source location. Each element has the data type specified by the Data type parameter.
Use offset when reading — Use offset when reading input
off (default) | on
Specify whether the block uses an offset when reading input. The offset value is in elements of the specified data type. Specify the source of the offset by using the Specify offset source parameter.
Parameter Dependencies
If you select this parameter, use Specify offset source to specify the source of the offset.
Use Offset to specify the offset value.
Specify offset source — Source of input offset
Specify via dialog (default) | Input port
Specify the source of the input offset for the copy operation. To specify an
offset value, select Specify via dialog. That selection
enables an Offset parameter that you use to specify the offset
value.
To specify for the block to get the offset from an input port, select
Input port. When you select Input
port, the block creates an input port labeled src ofs and
reads the offset value from that port. The src ofs port enables
your program to change the offset dynamically during program execution.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Use offset when reading.
Offset — Number of values to skip before copying first value to destination
0 (default) | positive integer
Before copying the first value to the destination, specify the number of values to skip.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Use offset when reading
and set Specify offset source to Specify via
dialog.
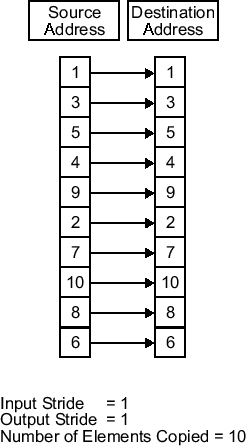
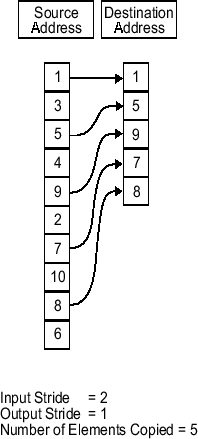
Stride — Spacing for reading input
1 (default) | positive integer
Specify the spacing for reading the input. By default, the stride value is one, meaning that the generated code reads the input data sequentially. When you add a stride value that is not equal to one, when reading input data, the generated code skips spaces in the source address equal to the stride.
These figures show the stride concept. In the first figure, data is copied without a stride. The second figure shows the results of a stride value of two. You can specify a stride value for the block output with parameter Stride on the Destination tab. You can also compare stride with the offset to see the differences.
Destination
Specify the destination memory location for the copy operation. Specify the attributes of the destination.
Copy to — Type of output destination for copy operation
Output port (default) | Specified address | Specified destination code symbol
Specify the type of output destination for the copy operation. Select one of the values listed in this table.
| Parameter Value | Destination of Data Write |
|---|---|
Output port | Block dst output port |
Specified address | Memory location specified by parameters Specify address destination and Address |
Specified source code symbol | Symbol (variable) specified by parameter Source code symbol |
Parameter Dependencies
If you select
Specified address, use Specify address destination to specify the destination memory location.If you select
Specified source code symbol, use Destination code symbol to specify the symbol (variable) in the source code symbol table to which to copy the variable.
Specify address source — Source of memory address for output destination
Specify via dialog (default) | Input port |
Specify the source of the destination memory address of the variable for the copy
operation. To specify a memory address for the variable, select Specify
via dialog. That selection enables an Address
parameter that you use to specify the memory address. To specify that the block get
the address from an input port, select Input port. When you
select Input port, the block creates an input port labeled
&dst. Changing the address dynamically means that you can use
the block to copy different variables by providing the variable address from an
upstream block in the model.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Copy to to
Specified address.If you select
Specify via dialog, this parameter enables the Address parameter, which you use to specify the address of the destination variable.
Address — Memory address of destination variable
hex2dec('00002000') (default) | memory address in decimal or hexadecimal form with a conversion to
decimal
Specify the memory address of the destination variable in decimal form or in
hexadecimal form with a conversion to decimal as shown by the default value
hex2dec('00001000').
This example converts Ox2000 to decimal form.
8192 = hex2dec('2000');For this example, you can specify the address as 8192 or
hex2dec('2000').
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Copy to to
Specified addressand Specify address
source to Specify via dialog.
Source code symbol — Symbol in source code symbol table
myVariableDst (default) | string | character vector
Specify the symbol (variable) in the source code symbol table to which to copy the variable. The symbol that you specify, must exist in the symbol table for your program. The block does not verify whether the symbol exists in the symbol table and whether you specify the symbol with valid syntax. Enter text that specifies the symbol exactly as it appears in your code.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Copy to to
Specified source code symbol.
Data type — Data type of variable
uint32 (default) | double | single | int8 | uint8 | int16 | uint16 | uint32 | int64 | uint64 | boolean | Inherit from source
Specify the data type of the source variable. To inherit the data type from the
source variable, select Inherit from source.
Use offset when writing — Use offset when writing output
off (default) | on
Specify whether the block uses an offset when writing output. The offset value is in elements of the specified data type. Specify the source of the offset by using the Specify offset source parameter.
Parameter Dependencies
If you select this parameter, use Specify offset source to specify the source of the offset. Use Offset to specify the offset value.
Specify offset source — Source of offset for output destination
Specify constant value (default) | Specify source code symbol
Specify the source of the offset for the output destination for the copy
operation. To specify an offset value for the destination variable, select
Specify via dialog. That selection enables an
Offset parameter that you use to specify the offset value.
To specify that the block get the offset from the input port, select
Input port. When you select Input
port, the block adds an input port labeled dst ofs and
reads the offset value from that port. The dst ofs port enables
your program to change the offset dynamically during execution.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Specify offset source.
Offset — Number of values to skip before writing first value to destination
0 (default) | positive integer
Before writing the first value to the destination, specify the number of values to skip.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Use offset when writing
and set Specify offset source to Specify via
dialog.
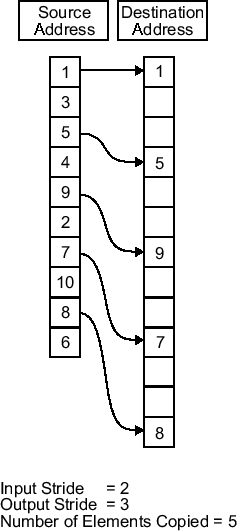
Stride — Spacing for writing output
1 (default) | positive integer
Specify the spacing for writing the output. By default, the stride value is one meaning that the generated code writes the input data sequentially to the destination in consecutive locations. When you add a stride value that is not equal to one, when writing input data, the generated code skips spaces in the destination address equal to the stride.
This figure shows a stride value of three applied to writing the input to an output location. You can specify a stride value for the input with parameter Stride on the Source pane. As shown in the figure, you can use an input stride and an output stride at the same time to enable manipulating memory more fully.
Sample time — Rate of memory copy
inf (default) | scalar
Specify the rate at which the memory copy operation occurs in seconds. To use a
constant sample time, specify Inf. To inherit the sample time from
the input port or, when the block does not have an input port, from the Simulink® model, specify -1.
Options
Configure parameters that control the copy process.
Set memory value at initialization — Set memory address during initialization
off (default) | on
Specify whether to initialize the memory address to a specific value during program initialization.
Parameter Dependencies
If you select this parameter, use a combination of parameters to configure the initialization value.
| What to Configure | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Source of the initialization value | Specify initialization value source |
| Initialization value as a constant | Initialization value (constant) |
| Initialization value as a variable | Initialization value (source code symbol) |
| Initialization value as a mask to manipulate register contents at the bit level | Apply initialization value as mask |
| Apply a mask value | Bitwise operator |
Specify initialization value source — Source of initialization value
Specify constant value (default) | Specify source code symbol
Specify the source of the initial value. To configure the source for initializing
memory as a specific value, select Specify constant value.
To configure the source as a variable (a symbol), select Specify source
code symbol.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Set memory value at initialization.
Use Initialization value (constant) or Initialization value (source code symbol) to specify the initial value.
Initialization value (constant) — Constant initialization value
1 (default) | scalar
Specify a constant value.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Set memory value at
initialization and set Set initialization value
source to Specify constant value.
Initialization value (source code symbol) — Symbol in source code symbol table
myInitValueVariable (default) | string | character vector
Specify the symbol (variable) in the source code symbol table to use for the initialization value. The symbol that you specify must exist in the symbol table for your program. The block does not verify whether the symbol exists in the symbol table and whether you specify the symbol with valid syntax. Enter text that specifies the symbol exactly as it appears in your code.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Set memory value at
initialization and set Set initialization value
source to Specify source code symbol.
Apply initialization value as mask — Apply initialization value as mask
off (default) | on
Specify whether to use the initialization value as a mask to manipulate register content at the bit level. Your initialization value is treated as a string of bits for the mask.
To define how to apply the mask value, specify a value for the Bitwise operator parameter.
To use your initialization value as a mask, the output from the copy must be a specific address. The output:
Can be a symbol
Cannot be an output port
Parameter Dependencies
If you select this parameter, use Bitwise operator to define how to apply the mask value.
Bitwise operator — Type of bitwise operation
bitwise AND (default) | bitwise OR | bitwise exclusive OR | left shift | right shift
Specify the type of bitwise operation to use as a mask to manipulate the memory value. Applying a mask to the copy process means that you can select individual bits in the result. For example, by applying a mask, you can read the value of the fifth bit.
Select one of the bitwise operations in this table.
Bitwise Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Apply the mask value as a bitwise AND to the value in the register. |
| Apply the mask value as a bitwise OR to the value in the register. |
| Apply the mask value as a bitwise exclusive OR to the value in the register. |
| Shift the bits in the register left by the number of bits represented by the initialization value. For example, if your initialization value is 3, the block shifts the register value to the left 3 bits. In this case, the value must be a positive integer. |
| Shift the bits in the register to the right by the number of bits represented by the initialization value. For example, if your initialization value is 6, the block shifts the register value to the right 6 bits. In this case, the value must be a positive integer. |
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Apply initialization value as mask.
Set memory value at termination — Copy memory during program termination
off (default) | on
Specify that your program copy memory during program termination. Copying a value in memory during termination occurs in addition to a copy during program initialization.
Parameter Dependencies
If you select this parameter, you can use Set memory value only at initialization/termination to limit copy operations to occur during program initialization and termination only.
Termination value — Termination value
1 (default) | scalar | vector | matrix
Specify a value to write to memory during program termination.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Set memory value at termination.
Set memory value only at initialization/termination — Copy memory value during program initialization and termination only
off (default) | on
Specify whether to perform copies during program initialization and termination only. When this parameter is cleared, the block performs copies during initialization, real-time operations, and termination. If you select this parameter, the block performs copies during initialization and termination only.
Insert custom code before memory write — Insert custom code before memory write
off (default) | on
Specify whether the code generator inserts custom ANSI C code immediately before the program writes to the specified memory location. You can use this parameter and Insert custom code after memory write to lock and unlock registers before and after accessing them. For example, some processors have registers that you might need to unlock and lock with EALLOW and EDIS macros before and after your program accesses them.
Parameter Dependencies
If you select this parameter, use Custom code to specify the custom ANSI C code to insert into the generated code immediately before the memory write operation.
Insert custom code after memory write — Custom code after memory write flag
off (default) | on
Specify whether the code generator inserts custom ANSI C code immediately after the program writes to the specified memory location. You can the Insert custom code before memory write and this parameter to lock and unlock registers before and after accessing them. For example, some processors have registers that you might need to unlock and lock with EALLOW and EDIS macros before and after your program accesses them.
Parameter Dependencies
If you select this parameter, use Custom code to specify the custom ANSI C code to insert into the generated code immediately after the memory write operation.
Custom code —
/* Custom Code Before Write*/ or /* Custom Code After Write*/ (default) | string | character vector
Specify custom ANSI C code to insert into the generated code immediately before or immediately after the memory write operation. Code that you specify appears in the generated code exactly as you enter it.
Parameter Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Insert custom code before memory write or Insert custom code after memory write.
Version History
Introduced in R2011a
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.

Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other bat365 country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- New Zealand (English)
- 中国
- 日本Japanese (日本語)
- 한국Korean (한국어)