Acquire Continuous and Background Data Using NI Devices
This example shows how to acquire analog input data using non-blocking commands. This allows you to continue working in the MATLAB command window during the acquisition. This is called background acquisition. Use foreground acquisition to cause MATLAB to wait for the entire acquisition to complete before you can execute your next command.
Create and Configure the DataAcquisition Object
Use daq to create a DataAcquisition object and addinput to add an input channel to it. This example uses an NI 9205 module in National Instruments® CompactDAQ Chassis NI cDAQ-9178. This is module 1 in the chassis.
dq = daq("ni"); addinput(dq, "cDAQ1Mod1", "ai0", "Voltage"); dq.Rate = 2000;
Plot Live Data as It Is Acquired
During a background acquisition, the DataAcquisition can handle acquired data in a specified way using the ScansAvailableFcn property.
dq.ScansAvailableFcn = @(src,evt) plotDataAvailable(src, evt);
Set ScansAvailableFcnCount
By default, the ScansAvailableFcn is called 10 times per second. Modify the ScansAvailableFcnCount property to decrease the call frequency. The ScansAvailableFcn will be called when the number of points accumulated exceeds this value. Set the ScansAvailableFcnCount to the rate, which results in one call to ScansAvailableFcn per second.
dq.ScansAvailableFcnCount = 2000;
Start the Background Acquisition
Use start to start the background acquisition.
start(dq, "Duration", seconds(5))
There are no other calculations to perform and the acquisition is set to run for the entire five seconds. Use pause in a loop to monitor the number of scans acquired for the duration of the acquisition.
while dq.Running pause(0.5) fprintf("While loop: Scans acquired = %d\n", dq.NumScansAcquired) end fprintf("Acquisition stopped with %d scans acquired\n", dq.NumScansAcquired);
While loop: Scans acquired = 1000
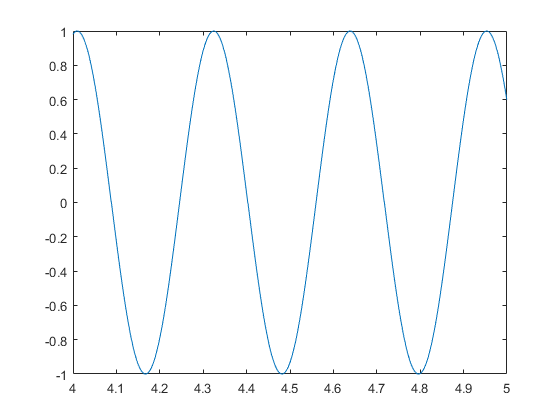
Capture a Unique Event in Incoming Data
Acquire continuously until a specific condition is met. In this example, acquire until the signal equals or exceeds 1 V.
dq.ScansAvailableFcn = @(src,evt) stopWhenEqualsOrExceedsOneV(src, evt);
Configure the DataAcquisition to acquire continuously. The listener detects the 1V event and calls stop.
start(dq, "continuous");
Use pause in a loop to monitor the number of scans acquired for the duration of the acquisition. Note that the status string displayed by the ScansAvailableFcn may appear before the last status string displayed by the while loop.
while dq.Running pause(0.5) fprintf("While loop: Scans acquired = %d\n", dq.NumScansAcquired) end fprintf("Acquisition has terminated with %d scans acquired\n", dq.NumScansAcquired); dq.ScansAvailableFcn = [];
While loop: Scans acquired = 1000 Detected voltage exceeds 1V: stopping acquisition While loop: Scans acquired = 2000 Acquisition has terminated with 2000 scans acquired
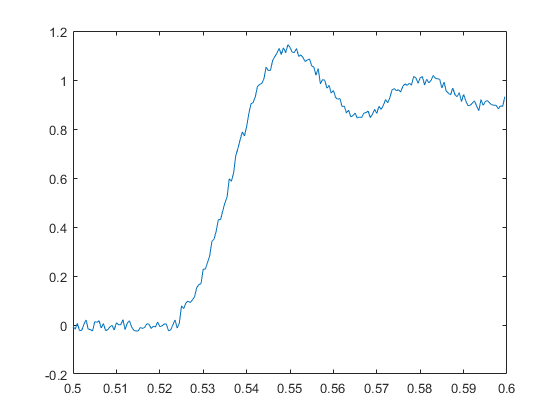
function plotDataAvailable(src, ~) [data, timestamps, ~] = read(src, src.ScansAvailableFcnCount, "OutputFormat", "Matrix"); plot(timestamps, data); end function stopWhenEqualsOrExceedsOneV(src, ~) [data, timestamps, ~] = read(src, src.ScansAvailableFcnCount, "OutputFormat", "Matrix"); if any(data >= 1.0) disp('Detected voltage exceeds 1V: stopping acquisition') % stop continuous acquisitions explicitly src.stop() plot(timestamps, data) else disp('Continuing to acquire data') end end
While loop: Scans acquired = 2200 While loop: Scans acquired = 3200 While loop: Scans acquired = 4200 While loop: Scans acquired = 5200 While loop: Scans acquired = 6200 While loop: Scans acquired = 7200 While loop: Scans acquired = 8200 While loop: Scans acquired = 9200 While loop: Scans acquired = 10000 Acquisition stopped with 10000 scans acquired
