Generate Code and Deploy MobileNet-v2 Network to Raspberry Pi
This example shows how to generate C++ code that uses the MobileNet-v2 pretrained network for object prediction. After generating the code, you can deploy it to a Raspberry Pi. This example uses the DAG network MobileNet-v2 to perform image classification with the ARM® Compute Library. The pretrained MobileNet-v2 network for MATLAB is available in the Deep Learning Toolbox Model for MobileNet-v2 Network support package.
When you generate code that uses the ARM Compute Library and a hardware support package, the codegen function generates code on the host computer, copies the generated files to the target hardware, and builds the executable on the target hardware.
Third-Party Prerequisites
ARM processor that supports the NEON extension
ARM Compute Library (on the target ARM hardware)
Open Source Computer Vision Library (OpenCV) v2.4 (on the target ARM hardware)
Environment variables for the compilers and libraries
The version of ARM Compute library this example uses may not be the latest version that code generation supports. For supported versions of libraries and information about setting up environment variables, see Prerequisites for Deep Learning with MATLAB Coder.
This example is not supported for MATLAB online.
Configure Code Generation for the mobilenet_predict Function
The mobilenet_predict function calls the predict method of the MobileNet-v2 network object on an input image and returns the prediction score output. The function calls coder.updateBuildInfo to specify linking options for the generated makefile.
type mobilenet_predictfunction out = mobilenet_predict(in)
persistent net;
opencv_linkflags = '`pkg-config --cflags --libs opencv`';
coder.updateBuildInfo('addLinkFlags',opencv_linkflags);
coder.updateBuildInfo('addCompileFlags',opencv_linkflags);
if isempty(net)
net = coder.loadDeepLearningNetwork('mobilenetv2', 'mobilenet');
end
out = net.predict(in);
end
Create a C++ code generation configuration object.
cfg = coder.config('exe'); cfg.TargetLang = 'C++';
The ARM Compute Library provides optimized functionality for the Raspberry Pi hardware. To generate code that uses the ARM Compute Library, create a coder.ARMNEONConfig object. Specify the version of the ARM Compute Library installed on your Raspberry Pi and the architecture of the Raspberry Pi. Attach the deep learning configuration object to the code generation configuration object.
dlcfg = coder.DeepLearningConfig('arm-compute'); supportedVersions = dlcfg.getARMComputeSupportedVersions; dlcfg.ArmArchitecture = 'armv7'; dlcfg.ArmComputeVersion = '20.02.1'; cfg.DeepLearningConfig = dlcfg;
Create a Connection to the Raspberry Pi
Use the MATLAB Support Package for Raspberry Pi Hardware function raspi to create a connection to the Raspberry Pi.
r = raspi;
If this is your first time connecting to a Raspberry Pi board or you want to connect to a different board, use this line of code and replace
raspinamewith the host name of your Raspberry Piusernamewith your usernamepasswordwith your password
r = raspi('raspiname','username','password');
Configure Code Generation Hardware Parameters for Raspberry Pi
Create a coder.Hardware object for the Raspberry Pi and attach it to the code generation configuration object.
hw = coder.hardware('Raspberry Pi');
cfg.Hardware = hw;Specify a build folder on the Raspberry Pi:
buildDir = '/home/pi';
cfg.Hardware.BuildDir = buildDir;Provide a C++ Main File
Specify the main file main_mobilenet.cpp in the code generation configuration object. This file calls the generated C++ code for the mobilenet_predict function. The file reads the input image, passes the data to the generated function calls, retrieves the predictions on the image, and prints the prediction scores to a file.
cfg.CustomSource = 'main_mobilenet.cpp';Generate the Executable Program on the Raspberry Pi
Generate C++ code. When you use the codegen function with the MATLAB Support Package for Raspberry PI Hardware, the function builds the executable on the Raspberry Pi.
For code generation, you must set the Environment Variables ARM_COMPUTELIB and LD_LIBRARY_PATH on the Raspberry Pi.
codegen -config cfg mobilenet_predict -args {ones(224, 224, 3,'single')} -report
Deploying code. This may take a few minutes. Code generation successful: View report
Run the Executable Program on the Raspberry Pi
To test the generated code on the Raspberry Pi, copy the input image to the generated code folder. You can find this folder manually or by using the raspi.utils.getRemoteBuildDirectory API. This function lists the folders of the binary files that the codegen funciton genereates. Assuming that the binary is in only one folder, enter:
applicationDirPaths = raspi.utils.getRemoteBuildDirectory('applicationName','mobilenet_predict'); targetDirPath = applicationDirPaths{1}.directory;
Use the putFile function to copy the files required to run the executable program.
r.putFile('peppers_raspi_mobilenet.png',targetDirPath);Run the executable program on the Raspberry Pi from MATLAB and direct the output back to MATLAB.
exeName = 'mobilenet_predict.elf'; argsforexe = ' peppers_raspi_mobilenet.png '; command = ['cd ' targetDirPath ';sudo ./' exeName argsforexe]; output = system(r,command);
Get the Prediction Scores for the 1000 Output Classes of the Network.
outputfile = [targetDirPath, '/output.txt'];
r.getFile(outputfile);Map the Prediction Scores to Labels and Display Output
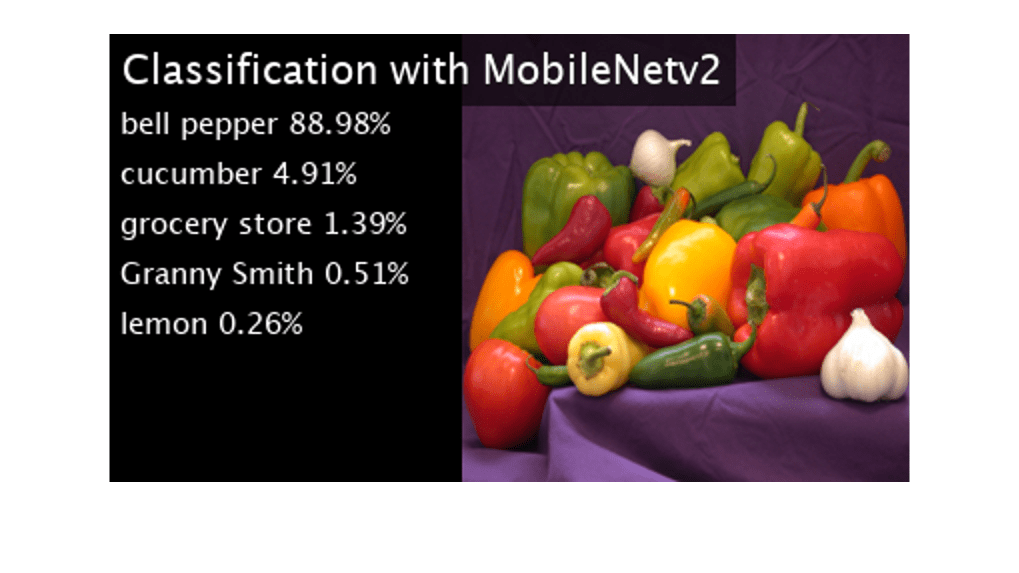
Map the top five prediction scores to the corresponding labels in the trained network and display the output.
mapPredictedScores_mobilenet
See Also
coder.ARMNEONConfig | coder.DeepLearningConfig | coder.hardware | coder.updateBuildInfo
