Stereo vision for depth estimation
Stereo vision is the process of extracting 3D information from multiple 2D views of a scene. Stereo vision is used in applications such as advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and robot navigation where stereo vision is used to estimate the actual distance or range of objects of interest from the camera.
The 3D information can be obtained from a pair of images, also known as a stereo pair, by estimating the relative depth of points in the scene. These estimates are represented in a stereo disparity map, which is constructed by matching corresponding points in the stereo pair.
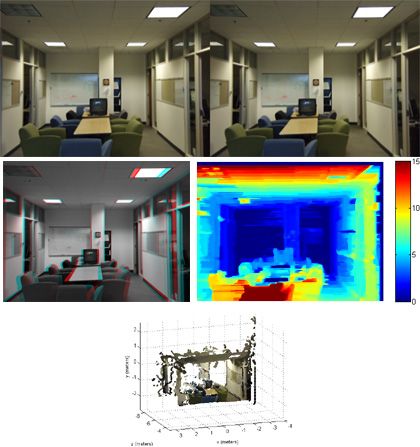
Reconstructing a scene using a pair of stereo images (top left and top right). To visualize the disparity, the right channel is combined with the left channel to create a composite (middle left). Also shown are a disparity map of the scene (middle right) and a 3D rendering of the scene (bottom center). See example for MATLAB code and explanation.
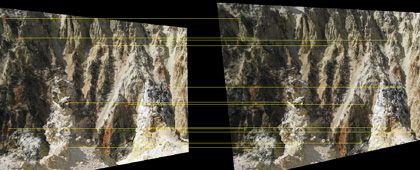
Rectified stereo image pair. Notice that matching points reside on the same row. See example for MATLAB code and explanation.

Stereo anaglyph showing calibrated stereo image rectification. See example for MATLAB code and explanation.
Stereo camera calibration (5:51) is used to determine the intrinsic parameters and relative location of cameras in a stereo pair, this information is used for stereo rectification and 3D reconstruction.
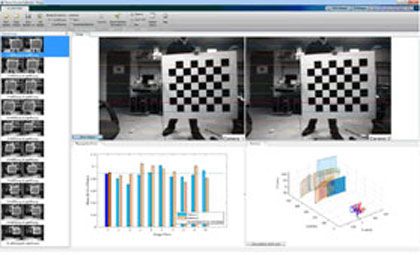
Calibrating a stereo pair using a checker board pattern using the Stereo Camera Calibrator App.
Stereo vision is also used in applications such as 3D movie recording and production, object tracking, machine vision, and range sensing. For more information on stereo vision, see Computer Vision Toolbox™.
Examples and How To
- Uncalibrated Stereo Image Rectification (Example)
- Calibrated Stereo Rectification (Example)
- 3-D Scene Reconstruction with Stereo Vision (Example)
- Measure Distance to Objects using Stereo Vision (Example)
- C Code Generation for Depth Estimation From Stereo Video (Example)
Software Reference
- Stereo Vision (Documentation)
- Stereo Camera Calibration (Tutorial)
- Disparity Estimation (Documentation)
- Triangulation with Stereo Vision (Documentation)
- Estimate Fundamental Matrix from Corresponding Points in Stereo Images (Function)
See also: object detection, image and video image processing, RANSAC, feature matching, feature extraction, RANSAC, point cloud, SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping), computer vision
