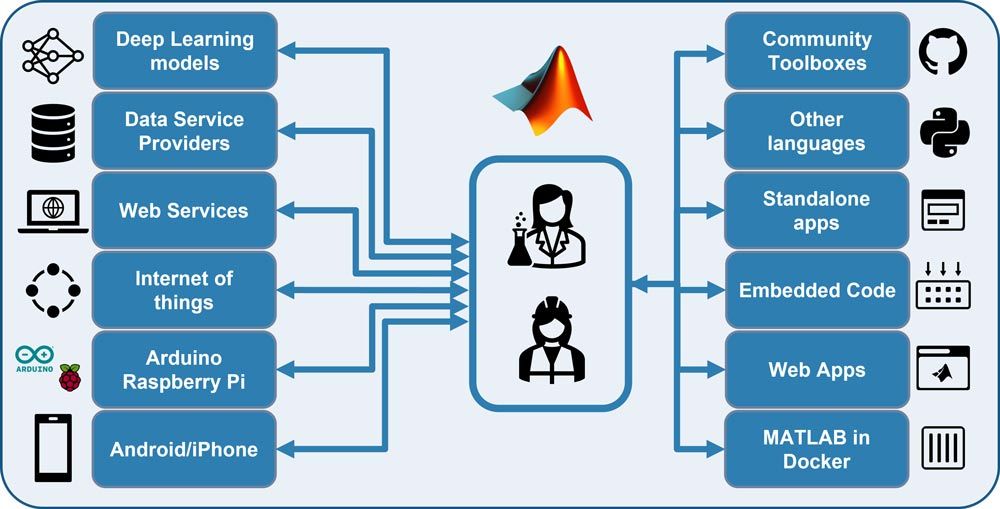
Share Methods and Output to Increase Impact
Open science is the practice of making scientific methodologies and output (such as publications, data, and software) transparent and broadly accessible. Open science maximizes the reuse of available data and code and enables scientists to build on the work of their peers.
Researchers using MATLAB® and Simulink® can practice open science to increase the scientific impact of their work.
Open Methods: Executable Notebooks
Well-documented methods and workflows enable open science by helping scientists follow each others’ experimental logic and interpret results.
Live Scripts
Using MATLAB live scripts, researchers can tell a story with data, code, and in-line visuals to make their work process and results transparent and easy to grasp. Researchers can:
- Incorporate images, text, equations, and hyperlinks with code in executable on-line notebooks
- Use interactive UI controls that allow fellow researchers to experiment with parameters and learn in a hands-on environment
- Publish in standard formats such as PDF, Word, HTML, and LaTeX
- Implement source control with Git and SVN to track changes and collaborate with others on projects
- Apply code and dependency analyses to map and organize large collaborative development projects
MATLAB with Jupyter
Jupyter® Notebooks are browser-accessible computational notebooks that are popular for open science projects. As with Python, MATLAB users can develop and run Jupyter Notebooks (.ipynb files) with an available MATLAB kernel and a MATLAB license.
To interact with a multi-user JupyterHub environment, you can install the MATLAB Integration for Jupyter to provide access to a full MATLAB desktop via a web browser for licensed users.
Open Data and Access
Providing access to data, models, and algorithms enables scientists to build on existing frameworks. Open science requires inter-operability between different data formats and programming languages, to ensure access across frameworks.
Open Access to Data
Publicly available datasets that can be accessed with MATLAB tools include:
- Allen Brain Observatory: The Brain Observatory Toolbox is an object-oriented interface for accessing neuroscience data from the Allen Institute
- EGI: Users can run MATLAB via shared online Notebooks that can access hundreds of data centers via the EGI cloud
- Climate Data Store: ECMWF users can download netCDF climate data files from Copernicus’ C3S and import the files into MATLAB for processing
Reading Data Formats
Standard data and model formats also support open science. MATLAB can:
- Work with data in popular data formats, including general scientific data formats, and many specialized data formats, including robotics, neuroimaging, medical imaging and time series analysis, biological sciences, meteorology, and geoscience
- Directly import deep learning models and ONNX™ model formats
- Read web application data in formats such as JSON, XML, and TXT via MATLAB RESTful web services
- Import and process data from connected devices in IoT systems by combining ThingSpeak™ and MATLAB
- Use Arduino® and Raspberry Pi™ to connect to data acquisition devices
- Harness sensors on Android™ or iPhone devices in experiments
Interoperable Code and MATLAB Algorithms
For open science, open access to data must be accompanied by open access to code and algorithms that generate meaningful results from these data.
- The bi-directional MATLAB integrations with Python, C, FORTRAN, and other languages enable algorithms written in one language to be called from the other
- MATLAB web apps enable sharing custom tools with non-MATLAB users
- With MATLAB Coder™, users can generate C and C++ code for a variety of software and hardware platforms, including embedded systems
- MATLAB Compiler™ enables sharing MATLAB applications as standalone applications, allowing end-users to run them without a MATLAB license
Open Code
A main motivation for open science is the reuse of scientific artifacts and algorithms. Sharing code and software helps colleagues build on each other’s work.
Open MATLAB Code on File Exchange
Researchers can freely access, download, and use MATLAB code and algorithms shared by their peers on File Exchange, or access them via the Add-Ons button on the MATLAB toolbar.
Toolbox authors can share their algorithms by linking to the GitHub repositories from File Exchange, ensuring a single code source with added visibility. File Exchange repositories linked to GitHub will automatically connect to the latest GitHub version.
Open MATLAB Code on Reusability Portals
Several reusability portals for open science offer a home for code where researchers can run uploaded code and reproduce results in the cloud, regardless of whether the researchers have a MATLAB license.
- Code Ocean: Contains runnable MATLAB code capsules associated with research papers
- Whole Tale: Hosts reproducible research artifacts or “tales” (MATLAB tales are accessible using a browser-based MATLAB desktop, Jupyter Notebook running MATLAB, or Linux web desktop)
- BioLib: Converts shared MATLAB code to web apps for use with data in a secure environment
Open Science Infrastructure
As researchers increasingly connect and collaborate remotely, open science requires infrastructure beyond an individual’s local workstation.
Runnable Code via Web Browser
Online access to coding environments makes scientific resources portable and accessible on the web.
- MATLAB Online and Simulink Online provide access to MATLAB over the web, without installation or download
- File storage on MATLAB Drive allows researchers, educators, and students to collaborate remotely on projects and exchange artifacts
Access to MATLAB and Simulink from any standard web browser, with no downloads or installations required.
MATLAB on Public Clouds and Services
MATLAB is accessible on various services used in open science.
- MATLAB works with cloud platforms, such as AWS and Azure, so users can scale up to take advantage of cloud compute services or access data stored in S3 containers
- Data science researchers use the Domino Data Lab platform to run MATLAB algorithms on centrally hosted data for scalable computing
- HPC centers such as Compute Canada and SNIC also offer MATLAB
MATLAB in Docker Containers
Containerized code is portable and reusable for open science. Available MATLAB containers include:
- A prebuilt MATLAB container on DockerHub, configurable with a built-in interactive IDE
- A prebuilt MATLAB Deep Learning Container on NVIDIA NGC Cloud
- Researchers can also build custom Docker containers with MATLAB
Science Gateways
Science gateways are online collaboration portals where scientists and engineers access shared resources. To enable open science, bat365 and many science gateways have collaborated to make community-contributed MATLAB-related content and MATLAB compute available.
Flexible Licensing for More Coverage
Many universities and research institutes have adopted campus-wide and Institute-wide MATLAB licensing models to provide MATLAB access to all their affiliated members. In keeping with open science principles, academic institutions can also provide access to MATLAB by external collaborators working on a project.
Open Science in Education
Open science is not limited to research, and practices include making scientific output and methods available and accessible to students and educators. Examples of publicly accessible resources for educators and students are:
- Resources for teaching computation in science and engineering with MATLAB via the Science Education Resource Center (SERC) curriculum portal
- STEM support: Student competitions, partnerships, and curriculum development
- Open and fun programming for children with Bytes and Beats courseware
Examples and How To
Software Reference
See also: shareable, reusable, MATLAB code, educator curriculum content